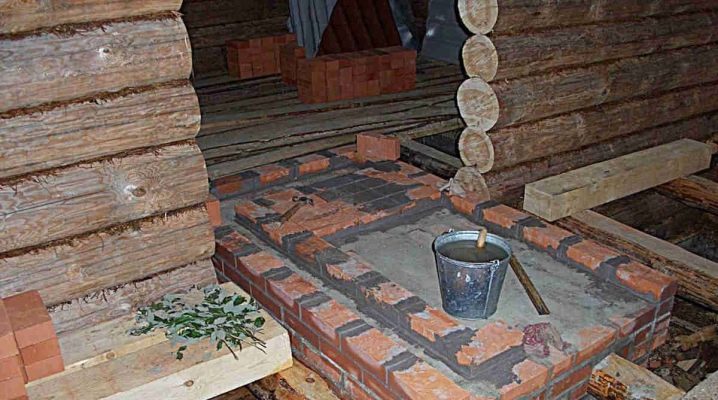
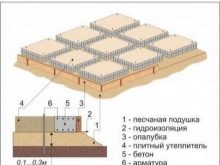
The process of making the foundation for the furnace
A real brick or “Russian” stove has been and remains one of the main elements of the interior decoration of many private houses and buildings. For some people, it plays the role of an original design solution, for others it only performs the function of heating. One of the highlights in its installation is the process of making the foundation.
Special features
Installing a working and reliable stove has some special features. For example, many developers or owners of private territories often wonder about the need to prepare the foundation or foundation for a furnace. This means both costs and additional construction work - in the case of buildings that have already been built.
The following factors will allow you to understand for yourself whether the installation of such a design is appropriate.
- Soil / soil characteristics. If you observe soil displacement, landslides or the formation of holes in the rock in your territory - the installation of the foundation is recommended. However, when installing the furnace in a house with a solid / solid reinforced concrete base, this option is excluded.
- Design features of the building / structure. Here such factors as the availability of free space for installation, the material at the base of the building (stone, wood, reinforced concrete) are important. In wooden houses with a brick stove without a foundation, there is a high risk of fire. Many types of bricks, such as porous clay, retain heat for a long time.
- Estimated weight of the stove. If it does not exceed 200-250 kg, the installation of the foundation is optional. It is worth considering the load of the furnace on the basis of your building / structure. Evenly distributing the weight is the same as ensuring a long shelf life for both the stove and the base. Equal pressure on both components will reduce friction and the risk of rapid wear. Since most of the furnaces are of the “Russian” type - dimensional constructions weighing up to several tons, this item is incredibly important.
Many people have their own opinion on this question, however, experienced developers understand the need to establish the foundation. This serves as an additional factor of reliability and stability of the stove.
Particular attention when installing the foundation should be paid to the type of soil in your area:
- sandy loam;
- clayey;
- loam.
Since the installation of a stove in homes most often is not a one-time use (except for less demanding and easy-to-install metal furnaces), it is worthwhile to take care of the preservation of the foundation at both high and low temperatures - for summer and winter time.
Some types of soil with clay content expand at low temperatures. In construction, this is called heaving, that is, freezing of moisture in the rock. However, the expansion of the soil is often uneven and can lead to cracks and damage to the foundation.
There are a number of measures for greater reliability in the installation of the foundation. They are designed for responsible owners or developers with established safety standards (construction of a public place: an estate, a museum, even a library).
- Supplying the foundation with an additional slab.The plate is placed under the base of the foundation, occupies a large area and has the function of reducing pressure and load. High-quality reinforcement of the slab is recommended, this will reduce the risk of cracking.
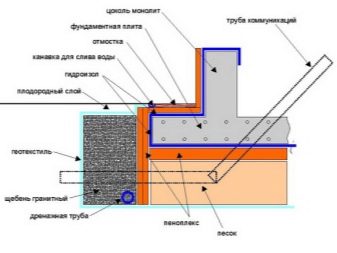
- When installing the slab, it is desirable to use a special sandy cushion, which will perform the function of damping (assuming pressure and loads) of the lower rocks during freezing.
- To ensure complete safety of the building, it is possible to install drainage pipes or to heat / insulate a building. This will reduce the possibility of excessive heaving.
This applies more to new buildings and structures under construction, but one should not think that the installation of an ordinary furnace is so complex and demanding.
Do not forget that the quality foundation for the stove is above all the safety for the whole house. The more quality efforts will be spent on its installation, the less will be the additional cost of time and resources for repair and dismantling.
Kinds
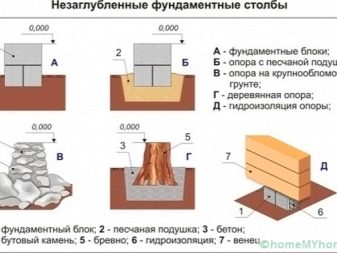
Weight, the presence of free space, the level of groundwater and the type of soil itself are the determining factors in choosing one or another type of foundation. You can find only a few types of foundation: tiled (or slab), pile, recessed / non-recessed. Some still talk about this type of tape foundation.
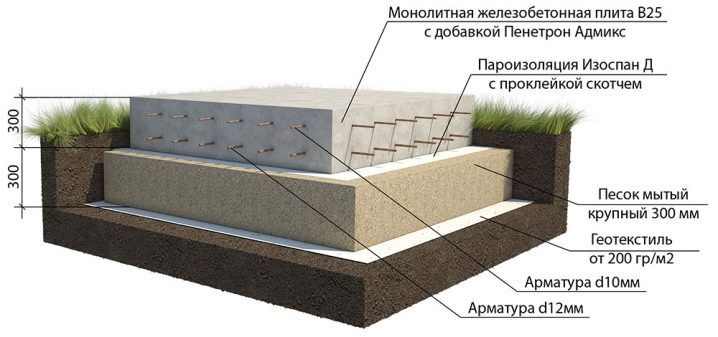
- Tiled the foundation requires the installation of sandy sand and crushed stone (up to 10 cm thick), filled with a concrete layer of no more than 5 cm, and reinforcement structures. They are set to evenly distribute the load. The peculiarity of the tile foundation is the solidity and integrity of the reinforced concrete / concrete slab. It is possible to place roofing material on bitumen, this will help the structure to maintain waterproofing.
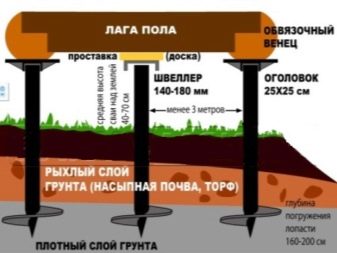
- The peculiarity of the pile foundation in simplicity and reliability. Its installation does not require additional excavation work - the piles can be driven into the ground by driving or vibrating. In this case, the piles can be made from some types of wood, and from reinforced concrete. Installation of metal hollow piles is possible - the design allows you to drive yourself deep into the ground and fill it with concrete - for better stability.
This type is one of the most common in the construction of buildings and objects of the average type.
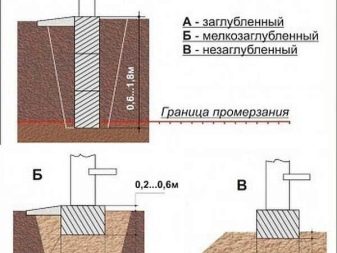
You can select the type of foundation for its placement relative to the floor of the building / structure. Here there is a buried type and a non-buried one.
- Recessed is needed for brick kilns with a weight of 2 tons or more. The basis for this foundation is porous clay or loess soil. The latter is a sedimentary rock of the non-layered type, often a mixture of loamy and sandy loamy rocks. In this case, do not forget that the depth of installation of the foundation on these rocks should be below the level of freezing in the autumn or winter frost.
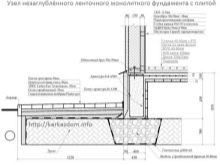
- The use of the non-buried type is justified for furnaces with a weight of not more than 1.5 tons. At the same time, it shows high characteristics of strength and reliability in areas with low groundwater levels and with continental or sedimentary ground rock.
Each type is used in different conditions at the construction site. Here we can say both about the weather conditions and the finances spent on the installation.
How to build?
Making each type of your own hands is quite possible, stock up with the necessary literature and patience.
The first step in a tile-type installation is to prepare a hole in the soil for future installation.The dimensions and depth in this case are not fixed by anyone (although there are recommended dimensions - up to 500 mm), the developer must independently select the optimal characteristics.
Should follow the surface of the pit, it should be flat.
The next stage is the filling of the pit with rubble (up to 10-15 cm) and compaction. It is possible to fill in ready solution after a waterproofing of a design with roofing material. The composition of the cast in this case is 1/3/5 (cement, sand, crushed stone). Often this type is installed on the ground floors of small buildings.
The pile foundation or the foundation on screw piles is no less reliable and easy to install. For it, you will need to dig holes in the corners of the proposed slab (the diameter must be kept at least 20 cm). Pits are pre-filled with moistened sand and gravel (from 10 to 15 cm) - this should be done for ease of tamping.
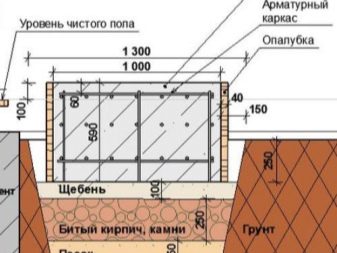
Preparation of formwork for further pouring of concrete requires the installation of a ruberoid sheet and armopoyas. After tamping, pouring and patching, the piles are mounted with each other and serve as bases for reinforced concrete or concrete slabs.As already mentioned, there is a type of pile foundation without excavation.
The recessed view is more complicated in the device and installation. There is a consistent installation plan.
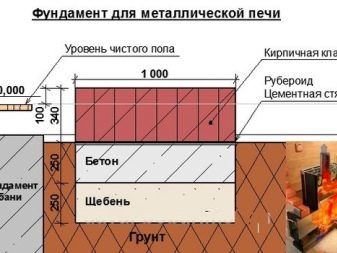
- Make sure that the ditch you dug was 10-15 centimeters larger than the size of the stove itself. This figure must be respected on each side of the pit. The depth characteristics in this case are not fixed, each follows different rules, but more often it does not exceed one and a half meters.
- The next step is to compact and tamp the bottom of the excavated pit. This can be used crushed stone (pre-moistened or not - you decide). After compaction of the bottom of the pit, the thickness of rubble should not fall below 15 cm.
- For tighter tamping, the developer can use a sandy layer up to 30 cm thick, the latter is moistened with a small amount of water for more compaction. When the sand layer dries, you need to add another layer of rubble on top of it. This time - up to 20 cm.
- The next important stage is to make wooden formwork. The inner surface can be pre-lubricated with bitumen, so you will provide waterproofing of your structure.
- Further installation of the recessed view is similar to the installation of the pile foundation, however, the formed space from the walls of the soil to the foundation in this case is filled with sand.
The non-buried type is represented by three separate types: a columnar, monolithic slab, a lattice. Each of these types has its own installation features.
- Columnar is a cheaper option and is presented in the form of several supports of the vertical type, immersed in the previously prepared soil by no more than 30%. The approximate distance between the supports should be 2 meters.
- Monolithic plate more suitable for installation of the foundation on the ground without subsidence of the soil. But this type is applicable to lighter buildings, as it is influenced by external factors - mechanical damage and others. Hydro- and heat-insulating elements can be placed under the finished monolithic slab - in order to avoid freezing in the winter season.
- Lattice type perhaps one of the simplest forms of a non-buried foundation. Making it consists of mounting a large number of plates with reinforcement. It will save your resources when pouring.In addition, the lattice type is more resistant to destruction. In the event of breakage or cracking on certain parts of the foundation, the risk of transferring damage to another part of it is reduced.
Tips
As you can see - the manufacture of the necessary foundation for the stove is a difficult but necessary process for the good operation of any heating system. There are several simple, summing up points, with the proper use of which you competently organize any furnace in your house.
- Determine the parameters of your territory. These are: environmental conditions, possible mechanical damage, calculate the load and pressure from the stove. Conduct a deep analytical calculation - from your financial capabilities to groundwater level measurements. The more accurate the data, the easier it will be to choose the appropriate type of foundation, and the less hassle it will bring you to its operation.
- Everyone has their own financial capabilities, but try not to save on technology, solutions and mechanisms for high-quality casting. Remember, the price is equal to the quality, and the more it is, the greater the chance that your installation will last a long time and will bring you only satisfaction and joy.
- Explore other resources, electronic and written with quality information about the installation of the foundation. You should understand that the one who is aware is armed with in case of unforeseen situations. And experience is not only a matter of theory, but also of practice.
The process of building a furnace from laying the foundation, see below.