Pile and strip foundation: advantages and disadvantages, recommendations for construction
The need to ensure the stability of capital buildings on moving or marshy ground causes a search for new foundation systems. Such is the pile-foundation, combining the advantages of two types of foundations.
Special features
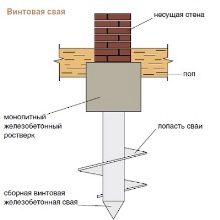
Pile-tape foundation is a tape base on the supports (piles), thereby achieving a stable design with a high margin of safety. In most cases, a similar foundation is created for large low-rise buildings on “problem” soils (clay, organic, uneven reliefs, water-saturated).
In other words, the strength of the structure is ensured by the ribbon (usually shallow-depth) foundation on which the walls are supported, and the strong adhesion to the soil is provided by the piles driven below the soil freezing level.
This type of foundation is not designed for multi-storey construction. Usually on such a foundation private houses are built no more than 2 floors in height with the use of lightweight materials - wood, cellular concrete blocks (aerated concrete and foam blocks), hollow stone, and sandwich panels.
For the first time, technology began to be applied in Finland, where predominantly wooden houses are being built. That is why the combined foundation is optimal for houses made of wood or frame structures. Heavier materials will require an increase in the number of bases, and sometimes the search for other solutions.
Most often, such a foundation is erected on floating clay, fine sandy soils, in swampy areas, poorly absorbing soil, and also in areas with a height difference (not more than 2 m in level).
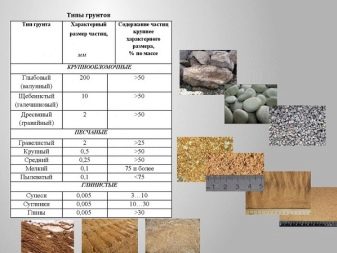
The depth of the pile is usually determined by the depth of the solid layers of soil. Monolithic concrete foundation is poured into the formwork, located in a trench 50-70 cm deep. Before starting work, make a study of the soil and punching test wells. On the basis of the data obtained, a scheme for the deposition of soil layers is drawn up.
The use of strip footing on piles allows to significantly increase the operational characteristics of the object under construction.
Among the advantages of the system are some positions.
- The possibility of capital construction on "capricious" soils - where it is impossible to use the strip base. However, due to the heavy load of the object, it will not be possible to use only piles.
- In this type of foundation, it is possible to reduce the sensitivity of the strip base to heaving soils and groundwater.
- The ability to protect the strip foundation from flooding, as well as transfer a large part of the base weight to the harder soil layers to a depth of 1.5-2 m.
- Such a foundation is also suitable for durable soils subject to seasonal deformations.
- Higher construction speed than the construction of the foundation with a deep foundation.
- The opportunity to get an object with a basement, which can serve as a useful or technical room.
- Accessibility of the use of materials used for the organization of the foundation, and for the construction of wall structures.
- Reducing the cost and complexity of the process compared with the organization of strip footing.
There are downsides to such a foundation.
- Increase when pouring the foundation of the number of manual operations. This is due to the inability to use excavators and other equipment for digging trenches due to hammered piles.
- The inability to use the resulting basement room as a full-fledged room (pool, rest room), as is possible with the device tape strip. This disadvantage can be leveled by digging a pit, but the cost and laboriousness of the process increases. In addition, this approach is not possible on every type of soil, even in the presence of piles.
- The need for a thorough analysis of the soil, the compilation of a large project documentation. As a rule, this work is entrusted to specialists in order to avoid inaccuracies and errors in calculations.
- A rather limited choice of building materials for the walls - this must necessarily be a light construction (for example, from wood, aerated concrete, hollow stone, frame house).
Device
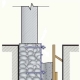
The load of the building on the ground is transmitted through a strip foundation, installed along the perimeter of the object and under its bearing elements, and piles. And support, and tape reinforced reinforcement.The installation of the first one is carried out by a bored method or by the technology of concrete pouring asbestos pipes installed in the wells. The drilled method also involves the preliminary drilling of wells into which the supports are submerged.
Today, screw piles are also spreading, having blades in the lower part of the support for screwing into the ground. The popularity of the latter is due to the lack of need for complex soil preparation.
If we are talking about screw piles up to 1.5 m, then they can be twisted independently, without the involvement of special equipment.
Drift piles are rarely used, since this method causes the appearance of ground vibrations, which adversely affects the strength of the bases of neighboring objects. In addition, this technology involves a high level of noise in the process.
Depending on the characteristics of the soil, piles-stands and hanging analogues are distinguished. The first option is characterized by the fact that the design of the pillars rests on solid layers of soil, and the second - the structural elements are in limbo due to the friction force between the soil and the side walls of the supports.
Payment
At the stage of calculation of materials, it is necessary to determine the type and number of piles, suitable for their length and diameter. It is necessary to approach this stage of work as responsibly as possible, since the strength and durability of the object depend on the accuracy of the calculation.
The determining factors in calculating the required amount of materials are the following positions:
- load on the foundation, including wind;
- the size of the object, the number of floors in it;
- features and technical characteristics of materials used for construction;
- soil features.
When calculating the number of piles take into account that they must be located in all corners of the object, as well as at the junction of the supporting wall structures. Along the perimeter of the building, the supports are installed in 1–2 m increments. The exact distance depends on the material of the walls chosen: for surfaces made of cinder block and porous concrete foundations it is 1 m, for wooden or frame houses it is 2 m.
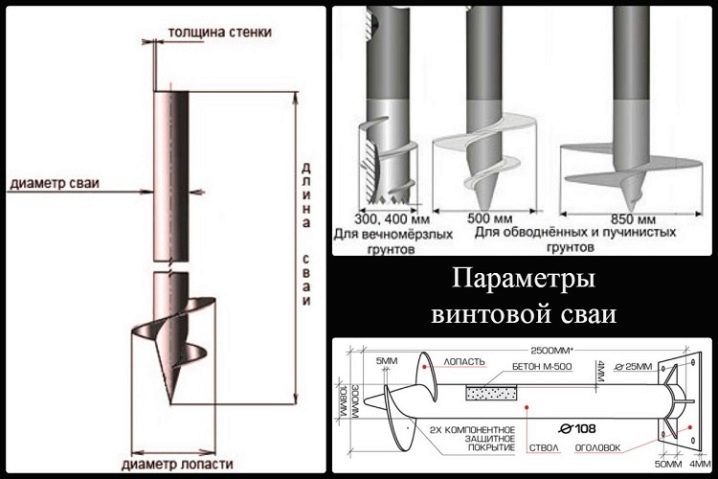
The diameter of the supports depends on the height of the building and the materials used. For a single-floor facility, screw supports with a diameter of at least 108 mm are required, for bored piles or asbestos pipes, this figure is 150 mm.
When using screw piles, models with a diameter of 300–400 mm should be selected for permafrost soils, 500–800 mm - for medium to heavy-toned, moisture saturated.
It is important that they have a corrosion-resistant coating.
Under the annexes - terraces and verandas - and heavy structures inside the building - stoves and fireplaces - we need our own foundation, fortified with supports along the perimeter. It is also necessary to install at least one pile on each side of the perimeter of the second (additional) foundation.
Installation
Getting to the implementation of the strip foundation on piles, it is necessary to conduct geological surveys - observations and analysis of the soil in different seasons. Based on the data obtained, the required load of the foundation is calculated, the optimal type of piles, their size and diameter are selected.
If you decide to create a pile foundation with your own hands, the attached step-by-step instructions will simplify this process.
- On the cleared site carry out a marking under the base. The tape trench can be shallow - about 50 cm. The bottom of the trench is filled with sand or gravel, which will ensure drainage of the concrete base and reduce the heaving of the soil.If we are talking about a large basement, the excavation is pulled out.
- At the corners of the building, at the intersection of the structure, and also around the perimeter of the building, with a 2 m step, drilling for piles is performed. The depth of the resulting wells should be 0.3-0.5 m lower than the level of soil freezing.
The diameter of the well should somewhat exceed the diameter of the support used.
- In the lower part of the wells, a sand pad 15–20 cm high should be created. Moistened sand should be moistened and tamped well.
- Asbestos pipes are inserted into the wells, which are first poured concrete by 30-40 cm, and then the pipes are lifted by 20 cm. As a result of these manipulations, concrete flows out, forming a sole. Its function is to strengthen the structure, ensuring better adhesion of the supports to the ground.
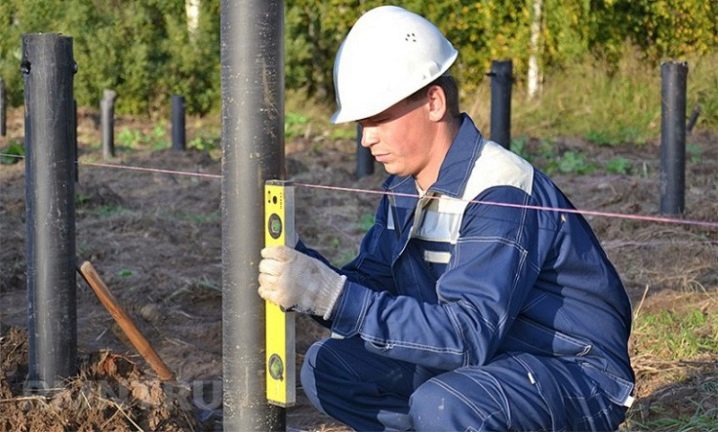
- While concrete is set, vertical alignment of the pipes is performed using a level.
- After solidification of the base of the pipe, its reinforcement is carried out - a grille is inserted into it, made of steel rods connected by metal wire.
The height of the grate must exceed the height of the pipe so that the grate reaches the top of the base tape.
- Wooden formwork is made on the surface, reinforced at the corners with bars and reinforced from the inside with reinforcement. The latter is a rod connected to each other by wire and forming a lattice. It is necessary to properly connect with each other reinforcement piles and tape - this ensures the strength and solidity of the entire system.
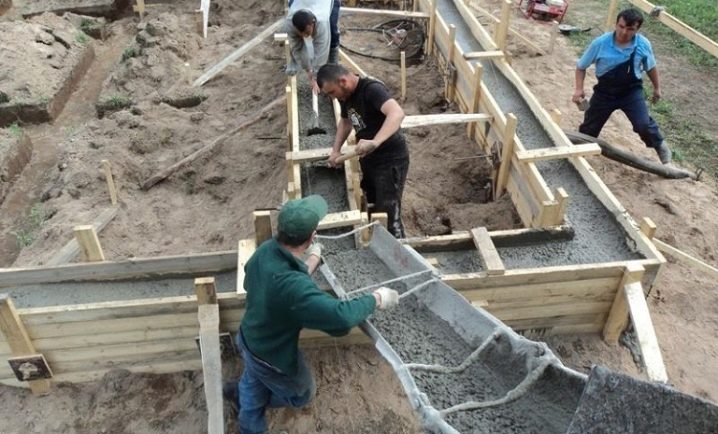
- The next stage - pouring piles and concrete formwork. At this stage it is important to pour the solution in such a way as to avoid the accumulation of air bubbles in the thickness of the concrete. For this purpose, deep vibrators are used, and in the absence of the device, you can use an ordinary rod, piercing the concrete surface in several places.
- The surface of the concrete is leveled and protected by covering material from the effects of precipitation. In the process of gaining concrete strength, it is important to observe the temperature and humidity conditions. In hot weather, the surface should be moistened.
- After the concrete has set, the formwork is removed. Experts recommend to immediately carry out waterproofing of the material, since it is hygroscopic. Saturation with moisture leads to freezing and cracking of the foundation.In this case, you can apply rolled materials (roofing material, modern membrane films) or bitumen-polymer coating waterproofing. To improve adhesion with the waterproofing layer, the concrete surface is pretreated with primers and antiseptics.
- The construction of the foundation is usually completed with its insulation, which allows to reduce heat loss in the house, to achieve a favorable microclimate. Foamed polystyrene plates glued to a special compound or polyurethane foam sprayed onto the foundation surface are usually used as insulation.
Tips
To achieve the smoothness of the outer walls of the tape allows the use of polyethylene. They are lined with the inside of wooden formwork, after which concrete solution is poured.
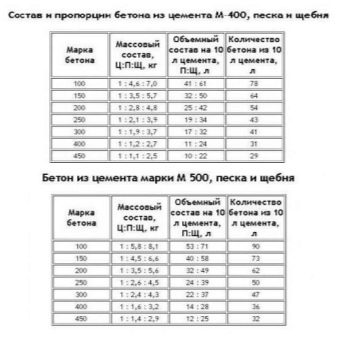
User reviews and professional advice allow us to conclude that the solution for casting should be prepared from cement of grade strength of at least M500. Less durable brands will not provide adequate reliability and solidity of the structure, they have insufficient moisture resistance and frost resistance.
The best solution is a solution of 1 part cement and 5 parts of sand and plasticizers.
When concreting it is unacceptable to drop the mortar into the formwork from a height of more than 0.5-1 m. It is unacceptable to move the concrete inside the formwork using shovels - it is necessary to rearrange the mixer. Otherwise, the concrete will lose its properties, and there is a risk of displacement of the reinforcing reinforcing lattice.
Pour formwork should be at one time. The maximum break in work should not be more than 2 hours - this is the only way to ensure the solidity and integrity of the foundation.
In summer, to protect against dehydration, the foundation is closed with sawdust, sackcloth, which is moistened from time to time for the first week. In winter, the heating of the tape is necessary, for which a heating cable is laid along its entire length. It is left until the foundation gains final strength.
Comparison of the strength of the reinforcement strapping with rods and welding allows us to conclude that the second method is preferable.
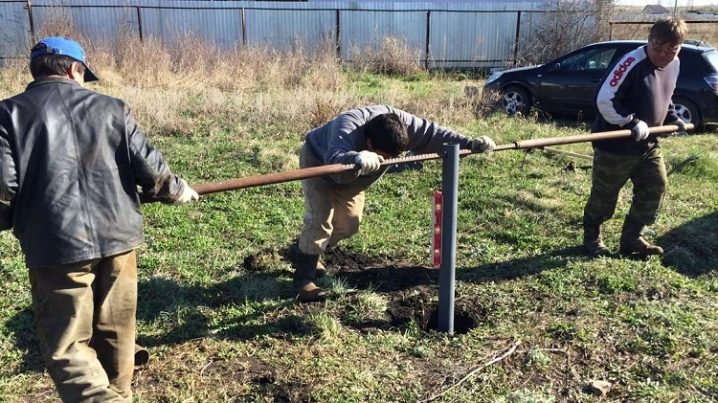
With the introduction of screw piles with your own hands, it is important to monitor their vertical position. Usually two workers rotate crowbars or levers, twisting the base, and another one monitors the accuracy of the position of the element.
To facilitate this work allows the preliminary drilling of a well, the diameter of which should be less than the support, and the depth - 0.5 m. Such technology will provide a strictly vertical position of the pile.
Finally, home craftsmen adapted household power tools for screwing in piles. This will require a drill with a power of 1.5-2 kW, which is held together with a pile by means of a special wrench-gearbox, characterized by a ratio of 1/60. After starting the drill rotates the pile, and the worker remains to control the vertical.
Before buying piles, you should make sure that the anti-corrosion layer is available and reliable. This can be done by examining the documentation attached to the products. It is also recommended to try to scratch the surface of the pile with a coin edge or keys - ideally, this will not succeed.
Installation of piles can be carried out at low temperatures. But this is possible only if the soil freezes to no more than 1 m. When freezing to a greater depth, special equipment should be used.
It is better to pour concrete in the warm season, as otherwise it is necessary to use special additives and heating the concrete.
About how to build a ribbon foundation with your own hands, you can learn from the following video.