Warming the foundation: how to do it right for many years?

Basement insulation is an important stage of home insulation, and also serves to protect the foundation from freezing and destruction. Insulation is better to carry out at the construction stage, but if necessary it can be done in an already constructed object.
The main thing is to comply with the installation technology in accordance with the type of building, foundation and materials used.
The reasons
Warming the foundation to prevent a negative impact on the external environment, which increases its service life, and hence the period of operation of the entire structure.
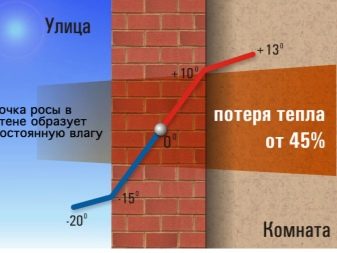
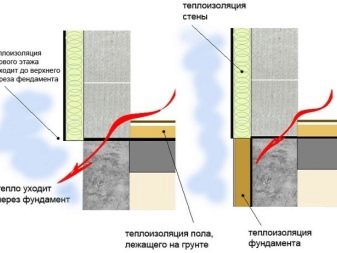
A large percentage of the heat loss of the object falls on the non-insulated foundation, even if its walls and roof have proper thermal insulation. When heat loss has to activate additional sources of heating, which leads to an increase in the cost of home maintenance. But most importantly, excessively heated air becomes dry. Being in such a room is uncomfortable, unhelpful.
Compulsory warming is meant in those basement and basement rooms that are used as boilers, pools, billiard rooms, etc. It is clear that in the exploited bases, the lack of heat makes it impossible to use the room. When located in the basement of communications, it is also important to ensure the proper level of temperature indicators, otherwise it is impossible to avoid their failure.
Pile foundations are also made to warm to reduce heat loss at floor level. To do this, they isolate the basement part, taking care to prevent the formation of “cold bridges” between metal and other elements.
Thermal insulation of the base allows you to avoid swelling of the soil, since the latter does not freeze around the foundation. This, in turn, helps to avoid fluctuations in the soil, causing shrinkage and sagging of the foundation, violation of its geometry.
As you know, each type of foundation has a certain frost resistance. For concrete foundations, the average is 2000 cycles. This means that the design withstands up to 2000 cycles of freezing and defrosting without losing its technical indicators. At first glance, the figure is quite impressive. However, in practice, several dozen freezing and thawing cycles can occur over one winter, which naturally reduces the durability of the base.
The use of heat-insulating materials allows to reduce the number of freeze / defrost cycles, because the foundation does not have time to freeze. As a result, the total number of permissible cycles is “consumed” less actively, and therefore the foundation will last longer.
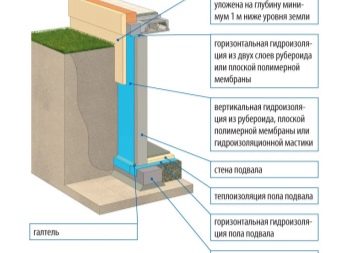
The insulation of the foundation of a private house or other object is carried out in conjunction with waterproofing, which allows extending the life of the structure, strengthening it, protecting it from the negative effects of groundwater and atmospheric phenomena.
Thus, we can conclude that the main functions of thermal insulation of the base of objects are to reduce heat loss and protect the foundation.
Which is more effective?
There are a considerable number of methods of insulation, but first of all it is necessary to determine whether the insulation is external or internal. Immediately it is worth making a reservation that experts recommend insulation outside, since this is a more efficient method.
It is external heat insulation that allows maximally (by 20-25%) to reduce heat losses, as well as protect the base. In case of internal thermal insulation, the surfaces do not accumulate heat; therefore, significant heat loss occurs. In addition, the non-insulated outside surface freezes through more (since it has no contact with a warmer basement or basement) and, accordingly, it collapses faster.
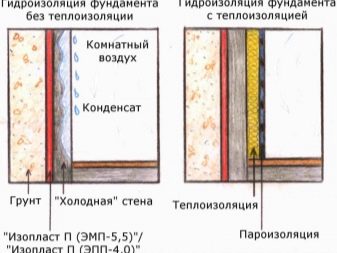
With internal insulation it becomes almost impossible to reduce the freezing of the soil and prevent its swelling. In addition, groundwater continues to affect the foundation. It turns out that thermal insulation from the inside only to some extent saves from heat loss, but in no way protects the base.
Besides, internal insulation reduces the useful area of the room, which may be important in the case of exploited basements. Finally, with internal thermal insulation, the vapor permeability of surfaces is almost always broken, as a result of which the room is filled with wet vapors, its microclimate is disturbed.
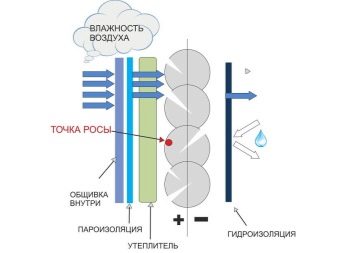
If moisture vapors do not have time to appear, they risk to settle on the surfaces of the foundation, insulation, finishing material. All this leads to their wet and loss of performance properties. Wooden surfaces begin to rot, corrosion appears on metal, erosion on concrete, insulation loses its thermal efficiency.
It is possible to prevent such phenomena by organizing a vapor barrier, as well as accurately calculating the thickness of the insulation. It is important that the dew point (the border where moisture vapor turns into droplets) falls on the outer layer of insulation or beyond.
Particular attention should be paid to the joints of the vertical surfaces of the foundation and the floor, floors, joints of surfaces, because with internal warming in these places there is a high probability of the appearance of “cold bridges”.
It should be noted that outdoor insulation is more effective, and therefore preferred.By internal experts recommend to resort only if it is impossible to implement other methods.
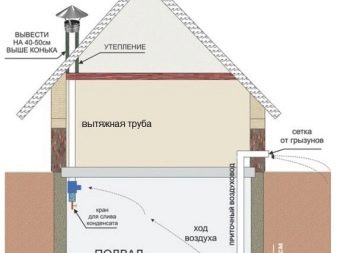
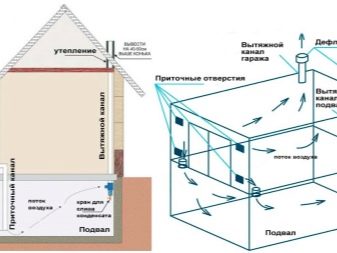
It is necessary to provide in this case high-quality vapor barrier, and in most cases (with a large area of exploited basements) - forced ventilation.
Another important issue that worries homeowners - when to warm the foundation. Ideally, this is done at the stage of its construction, after stripping or installing a grillage on a pile foundation. In this case, it is possible to achieve the maximum hermetic insulation, to produce better external insulation, as well as to reduce the complexity of the process.
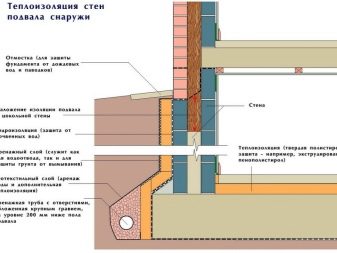
An important point in external insulation is the insulation of both the vertical surfaces of the foundation and the horizontal blind areas. It is during insulation during the construction phase that this recommendation can be implemented.
However, if this did not work out, we can also make insulation in an already built house.
How to insulate: ways
As already mentioned, you can warm any building. The choice of a particular method depends on what device has the foundation and the structure itself, how high the heat loss of the object.
Internal
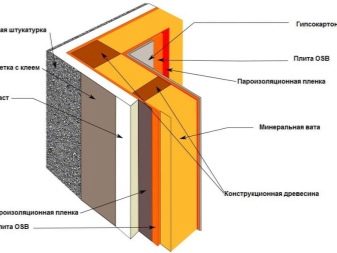
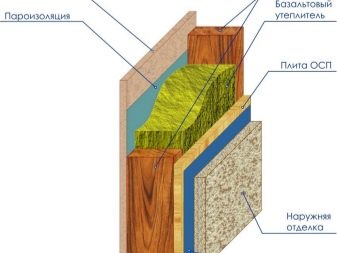
Internal warming as a whole is made by the same principles, as external.For this you can use foam polystyrene plates (not recommended for exploited premises due to their environmental insecurity), polyurethane foam spraying or penofol.
These heaters are mounted on a waterproofing layer, and then lined (by contact or on the principle of a ventilated facade).
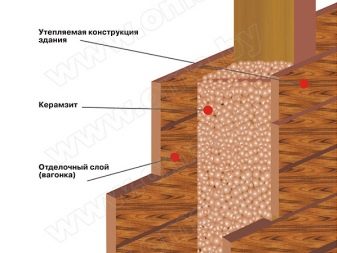
There is also a technology of warming with expanded clay, however, the layer thickness in this case must be at least 0.3 m. A wooden formwork with a height from the floor to the ceiling is created, which is waterproofed from the inside and covered with expanded clay.
Outdoor
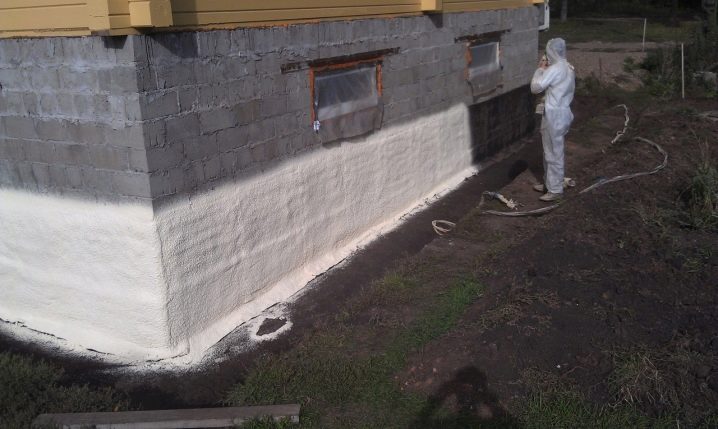
It assumes the release of the foundation from the ground, the restoration of its horizontals, the cleaning of surfaces. The most important step is waterproofing. Only over it is being heated. The materials and technologies used will be discussed below.
Under construction
As already mentioned, this is the most preferred option. It can be performed in 2 ways:
- to be a warmed fixed formwork;
- imply thermal insulation of the base immediately after its demolding.
In the first case, it is planned to create a formwork, the inner and outer walls of which are made of expanded polystyrene plates of suitable strength.The concrete mix is poured into the formwork in compliance with the technological requirements provided for the strip foundation, after which it is left for a month to build strength.
After the specified time, further work is performed.
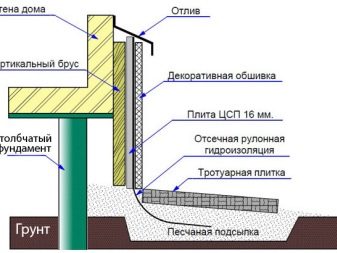
There is also a second method of insulation during the construction phase - formwork is also being prepared for this, which is poured with concrete. After the stipulated period of time, the formwork is removed (usually it is a wooden structure), the surfaces of the foundation, if necessary, are leveled and covered with a primer. Next, the base is waterproofed using bitumen-based roll materials. The next step is to warm the foundation, after which it is covered with protective and decorative materials (contact - paint, plaster, as well as hinged basement siding, panels, wall paneling, etc.).
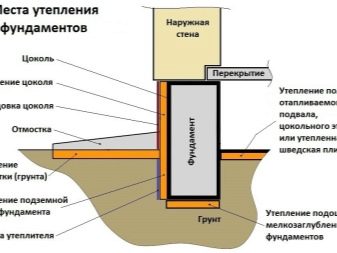
Foundations of a dwelling house
In general, the insulation of the basement of a residential house is similar to the insulation of just the foundation, but it involves a greater amount of earthwork, which will have to be done manually. The process involves the dismantling of the blind area and decorative trim basement.The next step is to dig a trench to the depth of the foundation. After that, you should prepare the foundation for insulation, if necessary, carry out or update the waterproofing and proceed to the installation of insulation. The work is completed by filling the foundation, installation of facade materials and blind area.
Old building
Old wooden houses often have no foundation. They were built immediately on the ground and put on several stones for reliability. However, over time, the lower part of the log house rots, sags. The situation can be improved by raising the frame with special jacks, restoring its geometry by replacing damaged wooden elements that are pre-treated with antiseptic compounds. Next, the house is put in place.
The use of polyurethane foam for insulating such buildings is questionable from the point of view of the thermal efficiency of this technology. At the same time, it is safe to say that the wood under this layer begins to rot much more actively.
If we are talking about old non-houses with a foundation, then the complexity of the insulation can be associated with strong uneven foundations.This is due to the lack of formwork during casting. In this case, they resort to warming with expanded clay.
To the depth of the foundation, a trench is also being dug, which is waterproofed and filled with expanded clay.
On top of it - 10 cm layer of sand, then restore the original appearance of the blind area.
Types and choice of material
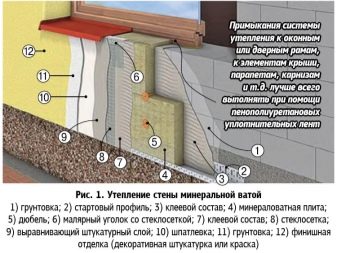
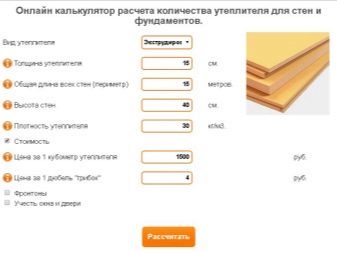
The most widespread for insulation as vertical surfaces, and the pavement, as well as a heater under the base plate received polystyrene foam. It has 2 varieties - well-known foam plastic and its extruded modification.
Preference is better to give the second option, since extruded polystyrene foam (EPP) has a better moisture resistance, less toxicity and greater fire resistance.
In terms of their thermal insulation features, all materials on a polystyrene foam basis exhibit a low thermal conductivity coefficient.
It is very convenient to use expanded polystyrene, since it is produced in slabs that have a smooth surface. Fixation is ensured by glue or bitumen mastic. It is important that the composition does not have solvents.
When working and storing the plates, it is important to remember that they do not tolerate exposure to UV rays. Otherwise, the material is destroyed. In this regard, immediately after installation of polystyrene heaters should be closed with a decorative layer or sprinkled with earth. If this cannot be done, it is necessary to provide temporary protection with covering material. Stored plates should be packed.
More modern insulation is polyurethane foam, which also has a low coefficient of thermal conductivity, differs in moisture resistance, durability, environmental friendliness and incombustibility. It is applied by spraying on the surface with a thickness of 3-10 cm. Due to the characteristics of the application, it is possible to achieve a monolithic layer - it penetrates into the smallest cracks, falls without joints between the elements. This is a guarantee of the absence of “cold bridges”. As a rule, professionals who have the necessary equipment are invited to perform the work.
As polystyrene products, polyurethane foam is destroyed by ultraviolet radiation. Another feature is the impossibility of contact coverage of the warmed surface,therefore, before spraying, it is necessary to mount a crate on which facade (socle) materials will be installed in the future.
Insulation with penofol is also a relatively new technology, which involves the use of roll material based on polyethylene foam. It has good thermal insulation properties and, moreover, has the ability to reflect heat.
The latter is due to the presence of a foil layer on one side.
Due to this, Penofol acts according to the principle of a thermos - it does not release heat from the room during the cold season and prevents its heating in the summer heat. In addition, the presence of foil coating increases the strength of the material, allowing it to keep its small thickness, provides additional waterproofing of surfaces.
As bulk insulation is usually used clay medium and small fraction. This natural clay-based insulation demonstrates high rates of heat and vapor insulation, characterized by non-combustibility, environmental friendliness and availability. However, it quickly absorbs moisture, so when using claydite, you should take care of additional waterproofing of the insulation layer.
Minvat, which has high thermal insulation characteristics, is rarely used because of its low moisture resistance and low material rigidity. An exception can only be high strength basalt fiber mats. However, they are also used to a greater extent as an internal insulant for exploited basements.
Requirements
The main requirement for insulation for the foundation, is a low coefficient of thermal conductivity. It is important that the material had high water resistance. That is why so popular mineral wool (which is not inferior to expanded polystyrene in its heat-insulating properties) is rarely used to insulate the foundation. She quickly gets wet and loses its qualities.
Only occasionally mineral wool is used as an internal insulation of the foundations in operation. However, in this case it is necessary to use more expensive basalt fiber, as well as diffuse membranes for steam and waterproofing. This layer is quite expensive.
Another important requirement for insulation is high strength.Since the material has to withstand increased mechanical loads (static and dynamic), resist to soil deformations.
Important when using wall insulation parameters of environmental and fire safety for foundation materials fade into the background.
The fact is that most of them are buried beneath the ground, which reduces the risk of fire and is used outside the building.
Specifications
Let us consider in more detail the most important characteristics of the above insulation for the foundation. Polystyrene plates with a heat loss coefficient of 0.037 W / m2K have the maximum thermal efficiency. For a clearer view of how good it is, let us give indicators of heat loss of air (the best heat insulator) —0.027 W / m2K, wood — 0.12 W / m2K, and brick — 0.7 W / m2K. Now it is clear that polystyrene foam surpasses almost all other materials in its thermal efficiency.
The heat loss coefficient of haydite is 0.14 W / m2K, polyurethane foam (depends on the type of working base and thickness) - in the range 0.019-0.03 W / m2K. The thermal conductivity of penofol is 0.04 W / m2K, while it is capable of reflecting up to 94-97% of thermal energy.
Plates based on extruded polystyrene foam do not absorb moisture, as well as polyurethane foam.
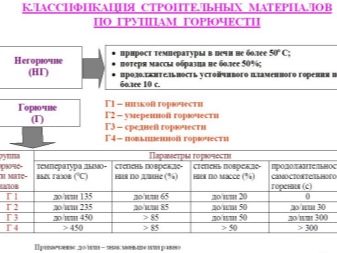
Polystyrene insulation has a flammability class G1-G4 (depending on the type, that is, it is flammable, releases toxins with increasing temperature), expanded clay and polyurethane foam have a flammability class NG (non-flammable), the latter, depending on the type, can also be classified as G1, G2.
Technology and stages of work
It is possible to get high-quality insulation only if the entire horizontal surface of the foundation and the vertical blind area are covered with thermal insulation material.
Regardless of whether the basement of the building object is being insulated or the socle of the house in use, the insulation must begin with the preparation of the foundation. To do this, it is cleaned from the ground over the entire surface, starting from the wall and ending with the base. A trench is formed around the entire perimeter of the foundation. Its width should be sufficient so that the workers in it can perform their functions.
In the construction site, the trench can be excavated with an excavator, in the finished house you will have to work manually with shovels.
The vertical surface should be cleaned from the ground and other contaminants, dry. If dents and cracks are detected, concrete bases should be embedded with a special polymer of operative action. Unlike cement mortars, they freeze after 12-24 hours.
In the presence of roughness and protrusions, it is better to repel them, and then walk on the surface with a grinding machine with a nozzle on a stone or wood.
The process will not be easy, but it is thanks to such work that we can achieve even surfaces that are as ready as possible for the next stage of work.
The considered actions are common to most types of foundations (including for bases on screw piles with a tape element).
The following stages of work vary depending on the type of foundation. Consider the features of technology characteristic of a particular design of the base.
Ribbon option
The prepared concrete surface is coated with a primer, which improves adhesion and will act as a kind of insulation for waterproofing. It is important to evenly cover the foundation with a primer and wait until it is completely dry.
The next step will be gluing or fusing waterproofing.It is mounted from top to bottom and also implies ultimately obtaining a monolithic coating without gaps.
After the organization of a layer of waterproofing proceed to insulation. To do this, often use polystyrene plates, which are applied adhesive composition. It is more convenient to do this with a notched trowel, calculating the amount of glue so that its excess does not protrude beyond the plate when fixed. If this happens, you should immediately wipe off the excess glue.
If necessary, the application of insulation in 2 rows of the second row is glued with a slight offset from the first. Row clearances should not overlap each other. When inter-seamless space appears, it is filled with construction foam, the surplus of which is cut with a knife after solidification.
For fixing polystyrene foam plates that are below the ground level, it is enough to use glue, because after falling asleep earth plates will be securely pressed to the surface.
That part of the insulation that falls on the base is additionally fixed with panned dowels. At the same time, a hole of the necessary diameter is drilled into the surface of the plates, after which the fastener is inserted into it.
Thermal insulation is completed by filling the basement and tamping the ground around, protecting the insulation with a decorative layer, if necessary, with a wind-winding film.
Pile
Thermal insulation of the pile foundation involves digging a trench between piles with a depth of 50 cm. A third part of it is covered with sand, and then a framework of reinforcement is made, which is poured with concrete. After the time required for its setting, the space between the overlap and the ground is laid with a brick around the perimeter while maintaining small ventilation gaps.
After that, the laying is covered with a layer of insulation (mainly EPP), reinforced with mesh and plastered.
Completes the process of decorating the plinth.
Columnar
The columnar foundation is insulated like a pile foundation. Instead of brickwork in both cases, you can use metal profiles or wooden bars. The first before use should be protected with anti-corrosion compounds, the second with antiseptics and antipyrine.
If necessary (harsh climatic conditions), perlite is added to the concrete solution or placed as a pillow interspersed with sand.
Slab
The slab foundation is insulated from the side that will be facing the inside of the house in the future. For this the base plate is covered with a waterproofing layer, and then a layer of insulation is laid (usually sheets of expanded polystyrene rugged or penofol). The layer of heat-insulating material is covered with plastic film, laid with an overlap of 10-15 cm and fixed with double-sided tape.
If in the future it is planned to fill the power floor, then it is made directly on the heat insulator protected by film and the knitted fittings laid on it to enhance the carrying capacity of the floor. If welded fittings are to be used, then first a floor screed (concrete or cement-sand) is made over the insulation and the protective film, and then welding works are carried out.
Tips masters
Properly insulate the foundation under the force of not every homeowner. Among the most common mistakes experienced masters distinguish the following:
- Lack of heat-insulating effect or its insignificant manifestation. The reason for this phenomenon is the insufficient thickness of the insulation, its getting wet or the preservation of "cold bridges".In any case, this is a serious mistake, which can only be corrected by dismantling the structure and redoing the work. Avoid trouble allows accurate calculation of the thickness of the insulation, high-quality waterproofing, compliance with technological standards during installation.
- Freezing corners of the basement. This is due to the insufficient thickness of the insulation layer on the horizontal surfaces of the blind area in these areas (namely, the corners and the adjacent surfaces are the most vulnerable). To avoid such an error again will allow an accurate calculation of the thickness of the insulation, as well as additional insulation in the corners of the object (the insulation is usually placed in 2 layers);
- High humidity in the technical basement or exploited base. This happens when trying to organize a warm base by internal warming.
To avoid problems will allow the presence of vapor barrier and a powerful ventilation system.
If such a nuisance happened during external insulation, it means that the technology for laying the facade material is broken (there should be a gap between the insulation and the insulation), there are no or insufficient technical holes, or they are in “dead zones” (for example, covered with snow).Problems can be avoided at the planning stage (having made the correct calculations in accordance with the SNiP) or by installing forced ventilation.
How to warm the foundation with your own hands, see the next video.