Features of gas silicate bricks
In the building materials market, silicate brick has appeared relatively recently, but has already managed to gain immense popularity among our compatriots. Its technical characteristics allow to erect buildings and structures that meet all modern quality criteria. And if we consider the material from the standpoint of price / quality, then gas silicate products will surely take one of the leading places.
What it is?
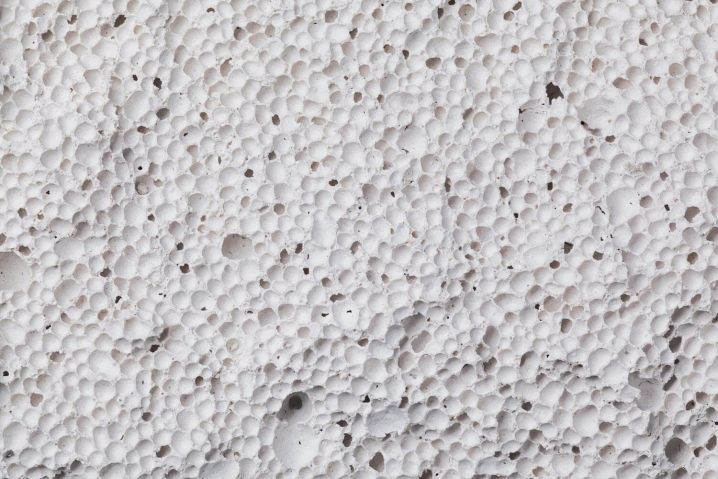
If to speak as simply as possible, the gas silicate brick is one of the varieties of porous concrete. At the exit, the material is quite porous, but at the same time its strength characteristics are fully consistent with the parameters of concrete. The main difference is in weight. Gas silicate blocks are less heavy - the parameter reduction is achieved due to the voids inside the pores.
In the 18th century, builders often added bull or pig blood to concrete and obtained a prototype of modern aerated concrete: when components were mixed, blood protein entered into a chemical reaction with other substances, and as a result foam appeared, which, when solidified, transformed into a durable building material.
One of the most famous engineers in the Soviet Union, M. N. Bryushkov, back in the 30s of the last century, noted that when squeezed plants were added to cement called the “soap root”, which grows in the republics of Central Asia, the mixture immediately starts to foam strongly and grow in size. When frozen, the porosity remained, and the strength increased significantly. However, the Swedish technologist Albert Erikson played the most significant role in creating the gas silicate. He created a unique technology for the production of material by adding gas-forming chemical components to cement.
Today, gas silicate bricks are made from cement with the addition of sand and hydrated lime. Then the mixture is passed through autoclaves and subjected to foaming with the addition of special magnesium dust and aluminum powder.
The finished substance is poured into forms, subjected to drying and hardening, which is achieved in two main ways:
- in natural conditions;
- in the autoclave under the influence of high temperature and strong pressure.
Better blocks are obtained by drying in an autoclave manner. In this case, they become more durable and resistant to external adverse conditions.
Thus, it can be seen that the gas silicate block is a rather uncomplicated composition of inexpensive and universally sold components, so the material is quite beneficial in housing construction.
Characteristics and composition
The composition of gas silicate material includes the following components.
- Portland cement of the highest quality, which is produced in accordance with the applicable State Standards. It consists of calcium silicate (its share is at least 50%), as well as tricalcium aluminum (6%).
- Regulatory sand. This brand is characterized by a minimum amount of silt and various clay inclusions, the content of which should be no more than 2%. Also includes quartz, about 7-8%.
- Technical water.
- Calcium lime, which is called the "kettle", to create porous concrete requires a composition not lower than the 3rd grade category. The rate of extinction of such a component is 10-15 minutes, while the percentage of burnout does not exceed 2%. Boiler also contains oxides of calcium and magnesium, the total share of which reaches 65-75% or more.
- Aluminum powder - is added for increased gas formation, materials like PAP-1 and PAP-2 are used.
- Sulfonic C is a component related to surface-active substances.
The composition and characteristics of the technology determine the properties of the material, among which they note both positive and negative.
The advantages of gas silicate bricks include the following characteristics.
- Low thermal conductivity. In the production of the material, the initial mixture is saturated with a large number of bubbles due to the content of the aluminum powder, when they freeze, they are converted into pores, which significantly affects the thermal conductivity. That is, the more pores, the better the material retains heat.
Let us explain with simple examples. If you live in the northern regions with harsh winters, then a 50 cm thick wall is enough to keep the heat inside the living space. You can have more, but as a rule, there is enough half-meter barrier.In places with a warmer climate, the thickness can be 35-40 cm, in this case, even on cool nights, the rooms will maintain a favorable microclimate and cozy atmosphere.
- Not less important feature of aerated concrete is good vapor permeability. If the humidity level in the room is higher than outside the house, then the walls begin to absorb excess moisture from the air and send it outside. If the situation is reversed, then everything happens exactly the opposite: gas silicate bricks absorb moisture from the outside and transfer it to the room, this is especially true when the heating is turned on, when the air in the heated room becomes too dry.
- For residential buildings is crucial fire resistance of the material. The walls of gas silicate can withstand contact with the flame for about 3 hours, as a rule, this time is enough to put out the fire, therefore, in case of fire, the chances of saving the house are quite large.
- The low weight of bricks also belongs to the undoubted advantages of the material. It is easy to transport, raise to a height, in addition, the design does not create a large load on the foundation, and this significantly increases the service life of the house.
- Gas silicate blocks are released from natural components, so the material is environmentally friendly. It is quite possible to use it in the construction of kindergartens and educational institutions, polyclinics, residential areas and other buildings, where the absence of toxic secretions is of fundamental importance.
- Well, a nice addition will be excellent sound insulation, which is possible due to the same porosity of gas silicate.
To make the most complete picture of the properties and characteristics of the material, it is useful to mention its shortcomings.
- The material has a rather low resistance to low temperatures. Without additional surface treatment, the composition withstands no more than 5 cycles of freezing and thawing, after which it begins to lose its strength rather quickly.
- Gas silicate complicates repair work, for example, it is impossible to screw the dowel into such a material, it starts to fall out immediately, and accordingly, even hanging a shelf in a house with gas silicate walls becomes a daunting task.
- In addition, the gas silicate does not adhere to the sand-cement plaster, so it’s impossible to finish the wall with such materialit will fall off in a very short time.
- The pores quite intensively absorb moisture and retain it within themselves. This leads to the gradual destruction of the material from the inside, and also creates an environment favorable for the reproduction of fungi, mold and other harmful bacteria.
However, with the correct processing of the material, many flaws can be leveled, so gas silicate does not lose its popularity among Russians. And the low price still becomes a decisive factor when choosing building materials in our difficult times.
Weight and dimensions
One of the main advantages of aerated building materials is their size, which is significantly larger than all other types of bricks. Due to these dimensions, the construction of buildings is much faster. According to some estimates, the advance can be up to 4 times, while the number of joints and connections is minimal, and this, in turn, significantly reduces all labor costs for construction and the consumption of fastening solution.
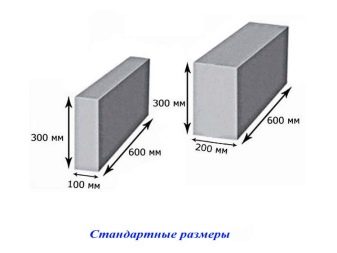
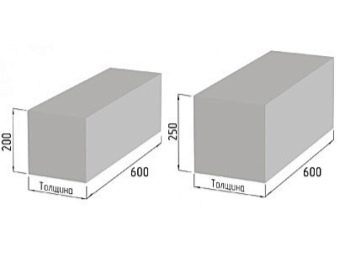
The standard size of gas silicate bricks is 600x200x300 mm. Also builders allocate a wall half block with parameters 600x100x300 mm.
Different manufacturers can find products with different parameters:
- 500x200x300 mm;
- 600x250x250 mm;
- 600x250x75 mm, etc.
In hardware stores you can almost always find products of exactly the size you need.
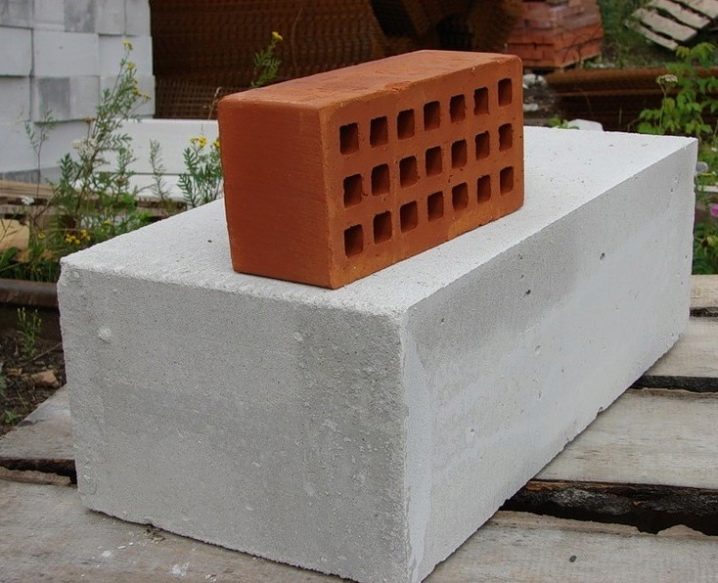
As for weight, the ratio here is obvious: the larger the brick, the greater its mass. Thus, the standard unit weighs 21-29 kg, the differences can be determined by the density of a particular foam block. Weight is one of the basic material advantages. Thus, the weight of 1 m3 of gas silicate is about 580 kg, and 1 m3 of ordinary red brick is 2048 kg. The difference is obvious.
Areas of use
Depending on the technical parameters of gas silicate bricks, largely determined and the scope of its use.
- Blocks with a density of up to 300 kg / m3 are most often used for insulation in wooden houses as the top layer.
- Blocks with a density of up to 400 kg / m3 are designed for the installation of load-bearing walls and partitions in one-story construction. It can be both houses and outbuildings.
- Gas units with a density of 500 kg / m3 will be optimal for buildings and structures in 3 floors.
- For multi-storey construction, blocks with an indicator of 700 kg / m3 are taken, and thorough reinforcement of the whole structure is required.
The use of gas silicate blocks allows to reduce the overall level of costs, while the structures are quite unpretentious in maintenance and operation. However, it is important that all technology is fully respected. Any deviations are fraught with the collapse of the building, so the lack of reinforcement or improper use of finishing materials can lead to a great tragedy.
Taking into account the fact that aerated concrete has a fairly affordable price, and its installation requires a minimum of time, you can even build a house with your own hands without attracting the labor of expensive hired professionals. Therefore, the material is often used for the construction of summer houses, small houses and baths. Let us explain with an example: a house of blocks is built at least 4 times faster than a house of bricks. In addition, when working with bricks, the presence of assistants is required, who will knead the mortar and bring in bricks, which, by the way, are much larger than blocks (in size one block is 16 bricks).
Thus, an obvious conclusion suggests itself - the use of gas-silicate blocks is profitable and economically justified, which is why in recent years many developers have made their choice in favor of this material. However, professionals recommend to adhere to some recommendations when using aerated concrete.
- When buying, you must personally check all purchased blocks. Different manufacturers allow deviations from GOST standards, therefore chipping, cracks and unevenness of the coating are often found on cheap bricks.
- When erecting 2 or more floors, it is necessary to install reinforcing supporting columns.
- Ceilings and walls of aerated concrete can not be left open, they require a mandatory lining, otherwise the performance of the material is significantly reduced every year.
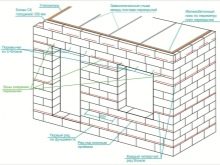
- Structures made of aerated concrete are strictly forbidden to build on soils with a weak bearing capacity. During construction, it is necessary to equip the strip foundation; it is optimal for works using such materials. Keep in mind that gas silicate is a rather fragile material, therefore, with any displacement of soil, it begins to crack, so when building a house, it is important to correctly calculate all the parameters of the foundation and select the most resistant brand of concrete.
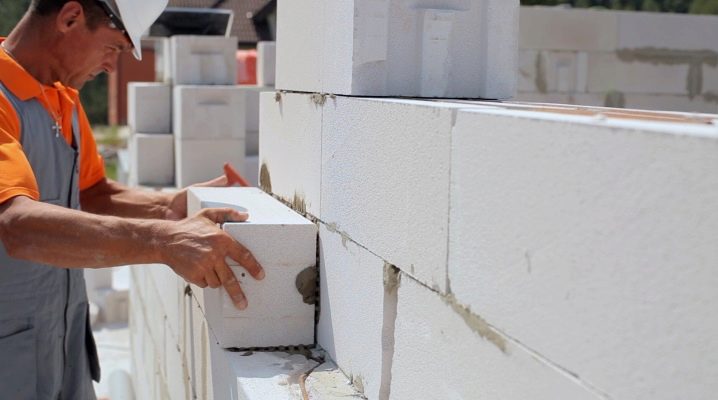
- When forming the first row of masonry, it is imperative to make high-quality waterproofing of the base in order to completely eliminate the ingress of moisture into the walls.
- The required size of gas silicate blocks should be calculated in advance, the seams should not coincide, as this may lead to a significant weakening of the masonry.
- Low density blocks can break down at high pressure, which means that before starting construction work it is important to calculate the load on the material and make a detailed plan-project.
For information on how a gas silicate block is used in construction, see the following video.