Polycarbonate greenhouses: pros and cons
The principles of planning zones in the summer cottage are such that at least 50% of the land is allotted for vegetables and a garden. But many plants from those that I want to plant on your site, designed for a subtropical climate. They need warmth, light and moderate humidity. With a deficit of these factors, the harvest is not rich.
Experienced gardeners have long found a way out using greenhouses. Assessing all the pros and cons of this building from different materials, we can conclude that the best option is polycarbonate greenhouses.
Special features
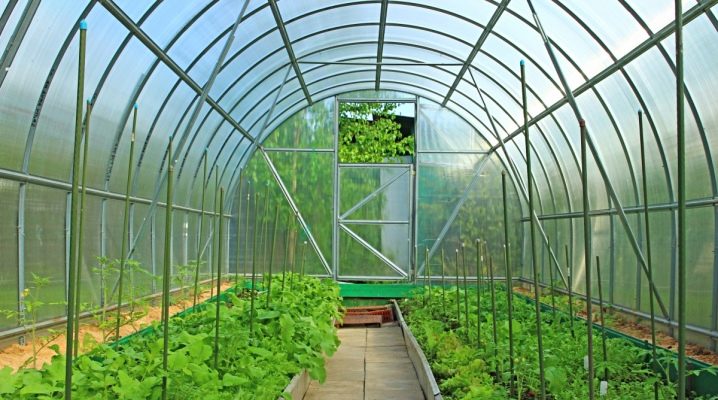
A greenhouse is often confused with a greenhouse - a temporary one-seasonal structure, the possibilities of which are severely limited. Unlike a simple greenhouse design - a frame and several layers of film, polycarbonate greenhouses have a number of distinctive features.
First of all, it is strength.The greenhouse has a strong metal frame, which is often purchased in finished form from the manufacturer. You can make the frame yourself from scrap materials, but without welding it will be less durable.
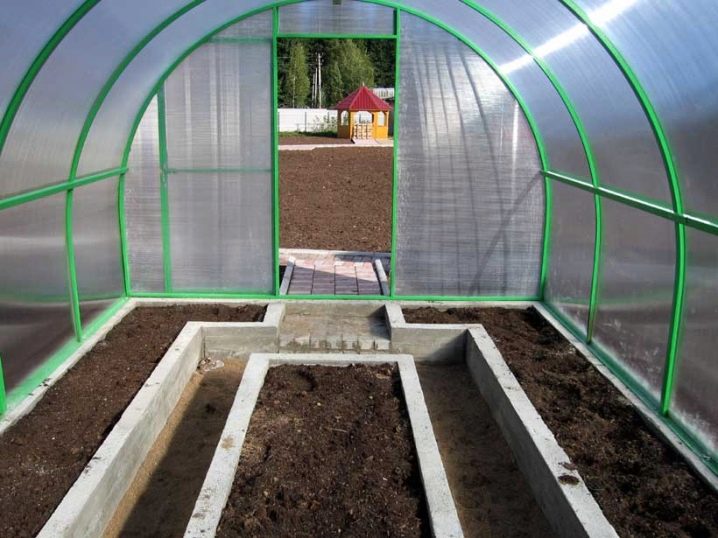
Partly the strength and stability of such a solid structure as a polycarbonate greenhouse provides the foundation.
Its presence defines another distinctive feature - the greenhouse is devoid of mobility. If the light temporary construction of hollow pipes and films can be rearranged from place to place, then the greenhouse is often static.
Another feature is its large size. In a greenhouse, a gardener can stand to his full height, move around without being constrained in his movements. In addition, a larger number of crops are placed in it and there is an opportunity to make several levels of plantings.
The microclimate inside the building can be maintained by the heating system. This is another factor that does not allow you to make it mobile. However, the presence of the heating system makes it possible to plant the seeds immediately into the ground in early spring. And due to the regulated level of heat, the range of crops grown is expanding.In a greenhouse made of polycarbonate, vegetables and greens sprout beautifully, not intended for a volatile Russian climate.
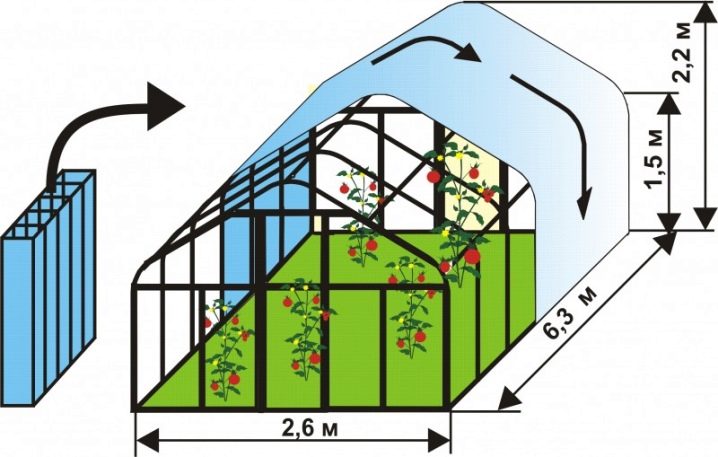
The greenhouse is distinguished from open ground by the fact that hot air accumulates in it. This obliges the gardener, who mounts such a device in his area, to make it high and to equip it with opening windows in the roof or the upper part of the walls.
Otherwise, instead of a rich harvest there is a risk of not getting anything.
Also in the design should be provided for ventilation, at least the most simple, in the form of two doors from opposite ends of the building.
Advantages and disadvantages
You can build a greenhouse or a greenhouse at your summer cottage using different materials: PVC film, glass, plastic, wooden and metal frame elements, various concrete bases. Depending on the type of material will vary the characteristics of the microclimate inside it.
Many gardeners are inclined to believe that polycarbonate is better suited for construction. It is flexible and resilient. This makes it possible to construct greenhouses of different geometric shapes with different types of roofs.
This material is durable and resistant to mechanical damage, does not freeze, does not crack with a sharp temperature drop and humidity levels.
It is moderately transparent. This means that the plants will have enough light, but at the same time the sun's rays do not heat the greenhouse and do not affect the greens like a magnifying glass, as it does with glass structures.
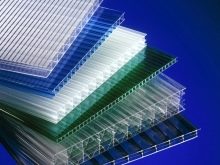
The structure of the material is cellular or monolithic. For covering greenhouses it is recommended to choose cellular (honeycomb) material. It provides voids and stiffeners, as in plastic windows. It is these air spaces inside the cells that provide the unique characteristics of polycarbonate greenhouses. The air does not allow the room to lose heat and freeze.
Polycarbonate is convenient to use when building. It can be cut and bent without the risk of damaging the cellular structure. This makes it convenient to do it yourself.
Finally, the material looks aesthetic. Such a greenhouse does not have to hide in the depth of the site from prying eyes. It will look beautiful that when using transparent polycarbonate, that when choosing a colored material.
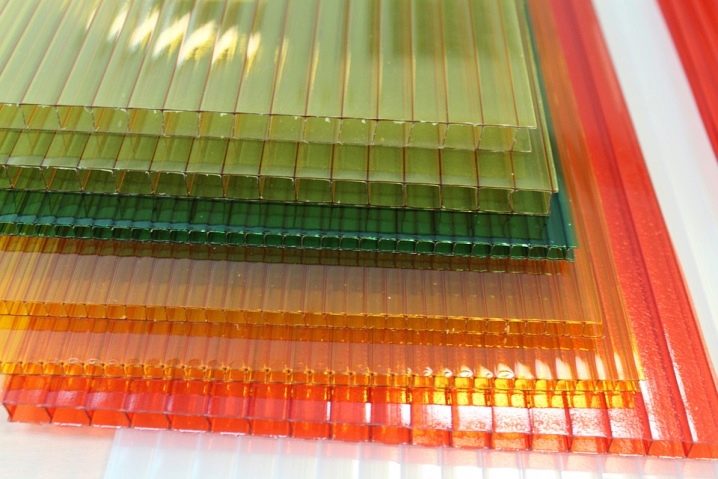
The color spectrum of the material is very diverse. Polycarbonate sheets are transparent, white, yellow, green, purple, orange, blue, red and gray. Hue may be more or less saturated.
It is important to bear in mind that the addition of a colorful pigment to the composition from which it is made is insignificant, but nevertheless reduces its resistance to freezing.
It becomes more fragile, so it is recommended to use a transparent or dim material.
The disadvantage of polycarbonate is the need for careful installation. Since open cells remain on the “slices” of the sheets, water can get into them, and this will lead to freezing in winter. In this case, the material may be damaged and be unusable by the beginning of the gardening season.
There is also a risk of damage to the material when using self-tapping screws as fastening the trim to the frame. In the place where the screw enters the sheet, too large a hole or cracks may form, which reduces the efficiency of the material. Through the cracks will get moisture inside, and heat loss will increase.
The advantages and disadvantages of polycarbonate as a building material are determined by the advantages of the structure:
- In the greenhouse, a full cycle of crop growth is possible: from planting seeds into the prepared soil to harvest.
- Inside creates a controlled microclimate for plants. In the cold season (in early spring and late autumn) it is kept warm, and in the warm season coolness is provided so that the herbs do not dry out. The humidity level is regulated in the same way. No matter how dry or rainy the weather is, the plants in the greenhouse will receive as much moisture as they need.
- There is an opportunity to grow crops that can not be grown in open ground. They even include berries and fruits from mainly the southern regions of the country: grapes, watermelons, apricots, citrus fruits and other types.
- Since it is possible to start planting plants much earlier than the beginning of the season, and finish much later, the greenhouse provides with its vegetables, berries and fruits not only in summer. You can harvest in one place twice in one season. At the same time, it is necessary to fertilize and cultivate the land so that it remains fertile.
- Conditions are suitable for crossing different cultures.
- The closed design protects the plants not only from hypothermia or the scorching sun, but also from "acidic" rain, wind, harmful insects, dust.
- Transparent material transmits sunlight, but not the ultraviolet rays of the harmful spectrum. This is facilitated by a special film coating.
- Polycarbonate has a long service life - 10-20 years.
- Greenhouse looks beautiful on the garden plot.
With all the positive aspects of the greenhouse has drawbacks.
- The design must be well thought out, planned and assembled. It takes time, skills and considerable financial expenses.
- Polycarbonate is not scratch resistant.
- The presence of a light-stabilizing layer (protection against UV rays) makes the material less durable. Its service life is reduced by several years.
- In the open ground, plants are pollinated by insects, without this there will be no harvest. In isolated conditions, it is necessary to take care of how this will happen, or to acquire self-pollinating varieties of plants. If the moisture and heat levels are not followed, the pollen will “dampen” and the plant will not give fruit.
- Two years in a row in the greenhouse can not grow the same plants. This is due to the fact that cucumbers, tomatoes and other vegetables have different pests. If you change crops in places, the pests die, the plants are not harmed.If from year to year to grow the same crops in one place, the harvest will deteriorate.
- In a polycarbonate greenhouse, if it is collected incorrectly, condensation may occur.
- Dark polycarbonate is worse than the sun. This prevents photosynthesis and good plant growth.
- The material expands and shrinks with changes in ambient temperature. If this is not taken into account during construction, cutting out the material with an expansion margin, in winter the greenhouse may crack in places of bends and fixings;
- Transparent polycarbonate becomes cloudy over time, and color fade. This is not the biggest problem on the background of the merits of the material, but as a result, the aesthetics of the building will suffer before the service life is out.
Kinds
An important stage in the arrangement of a polycarbonate greenhouse is to choose a type of this material.
The main criterion for this is the structure of the sheet. It can be monolithic (cast) or cellular (cellular).
Monolithic has a dense structure without an air gap. It can be smooth and wavy. In the first place in the list of its advantages is an aesthetic appearance - it looks like colored glass.When it comes to greenhouses, it looks quite unusual. In addition, the material is more resistant to scratches and damage, has greater strength and contributes to noise insulation. But for the rest of the characteristics, it is inferior to the cellular one. Due to its greater strength, it is more difficult to bend and cut, and the insulation does not play a role in the greenhouse.
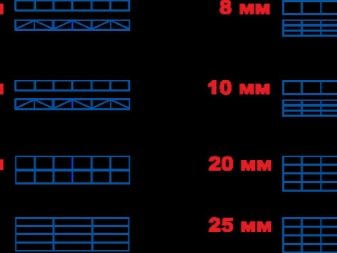
The structure of cellular carbonate implies cavities and partitions inside the sheet. On the cut, it resembles a honeycomb device, hence the name. Its thickness is 4-16 mm, depending on the type of sheet.
Sheet type is of several types.
- 2H - panels consisting of two layers. Honeycombs inside in the form of rectangles. Stiffeners - simple partitions. They are least resistant to wet snow load in winter; they are broken down by mechanical effects faster than other types. Easy to bend.
- 3H - three-layer panels with rectangular "honeycombs" and simple stiffening ribs. The ribs are arranged vertically. Sheet thickness - 6, 8 and 10 mm. Sheets of 6 mm are suitable for double plating of the greenhouse frame.
- 3X - three-layer sheets with combined stiffening ribs. Some have a vertical position, others - oblique.The average sheet thickness is 12-16 mm. The best option for covering greenhouses.
- 5W - sheets of 5 layers with a rectangular cell shape and vertical stiffening ribs. Thickness varies from 16 to 20 mm.
- 5X - five-layer sheets with stiffening ribs of direct and oblique type. They have the largest thickness - 25 mm. Suitable for covering greenhouses operating throughout the year and for arranging greenhouses in cold regions of the country.
Cellular sheets are more suitable for arranging greenhouses, as they slow down the process of heat loss and heating by the sun inside. They are more plastic than monolithic, and weigh less.
Constructions
Greenhouses are different in shape and type of construction.
The form of isolated and standing on the garden plot buildings and wall. The wall greenhouse is usually combined with a country house of one of the parties.
The advantage of the wall greenhouse is that it freezes less in winter due to its location. It is also possible to lay the foundation for the greenhouse simultaneously with the construction of the house. This simplifies the work and saves materials and space in a small area.
The lack of construction near the wall is that in such a greenhouse it is more difficult to organize uniform ventilation and air circulation.
In addition, the constant humidity and heat inside the building adversely affects the condition of the wall of the house. And in winter, the snow from the roof of the cottage can fall on the roof of the greenhouse. If it is not cleaned regularly, it can lead to the fact that the greenhouse will become unusable after a year or two.
There is also a division of structures into stationary and collapsible. Stationary greenhouses are more convenient, since they will need to be installed once every ten years.
Do collapsible also has its advantages: they can be moved from year to year to different places on the site, which will be useful for plants that can not be planted two years in a row in one place. Also, folding and sliding structures can be removed for the cold season and not worry about their safety.
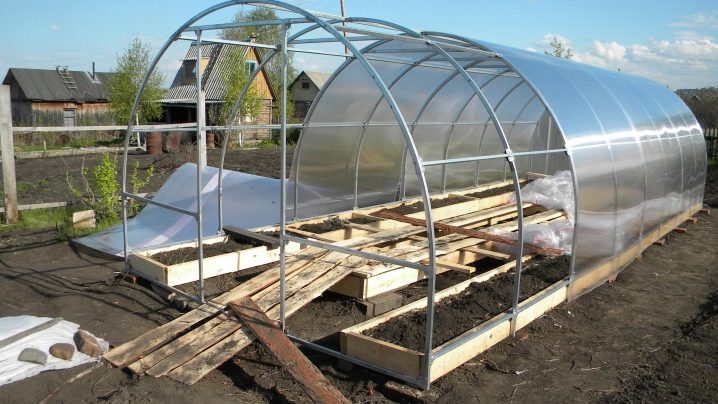
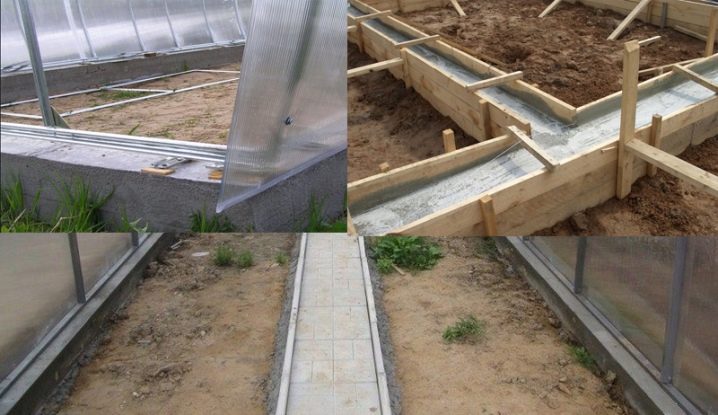
Foundation
The foundation is what makes the greenhouse sustainable, durable and different from other structures of similar purpose. Besides the fact that it adds strength, it retains about 10% of the heat inside, protects the ground from being washed out by rain, and protects plants from frost.
There are several types of foundation.
Solid
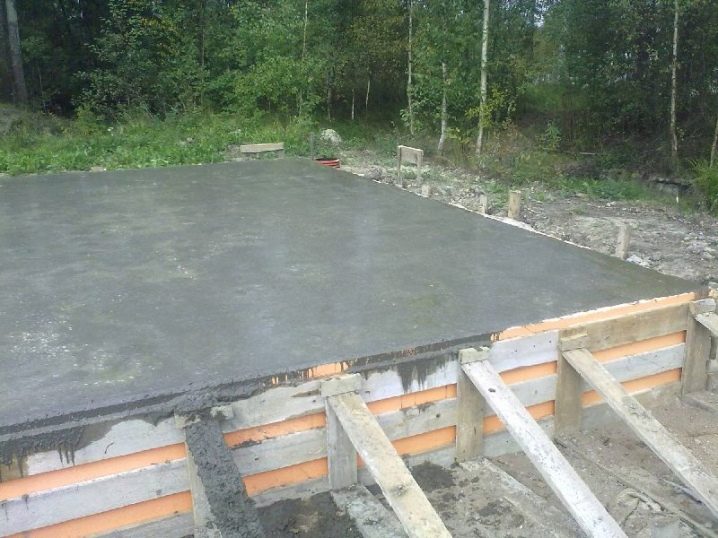
Such a foundation is considered the most time-consuming in the arrangement, since it completely covers the soil and requires re-organizing the fertile layer on top of the cement fill.It is needed in areas where groundwater rises too high, causing the plants in the soil to rot. Also, with the help of a solid foundation, you can level hilly areas of the earth.
It is done as follows: the fertile layer of soil is removed, they dig a hole in the ground by 15–20% more in area than the greenhouse, sprinkle with sand and tamp it tightly, lay waterproofing. The layer of sand cushion should be 15-20 cm thick. Waterproofing on top is obligatory - it will protect the foundation from destruction by groundwater. Above the waterproofing poured foundation of frost-resistant cement. The foundation itself must be reinforced with a metal grid so that it does not crack under the weight of the greenhouse and the ground. From above it is possible to establish the greenhouse.
Its height must take into account that a layer of fertile soil will be artificially formed on top of the cement. An alternative option for uneven terrain - the foundation on piles.
Tape
This type is much easier to create. A hole is dug in the ground (to the depth of soil freezing) in terms of the size of the greenhouse frame. Then these trenches are sprinkled with sand, equipped with waterproofing,and ready-made cement blocks are laid on top. They are strong enough, so the inner perimeter can not fill.
Columnar
For greenhouses, this option is rarely used, mainly, it is necessary for arranging a summer house in the country. The reason is that this method allows you to pour the foundation for the construction of complex polygonal shapes, which rarely applies to greenhouses.
The column base is laid almost identical to the ribbon base, but there is a slight difference. If the tape completely fills the grooves in the ground and the frame touches it at all points of support, then cement columns can be installed only at the corners of the frame. An important condition: the weight of the greenhouse should be small.
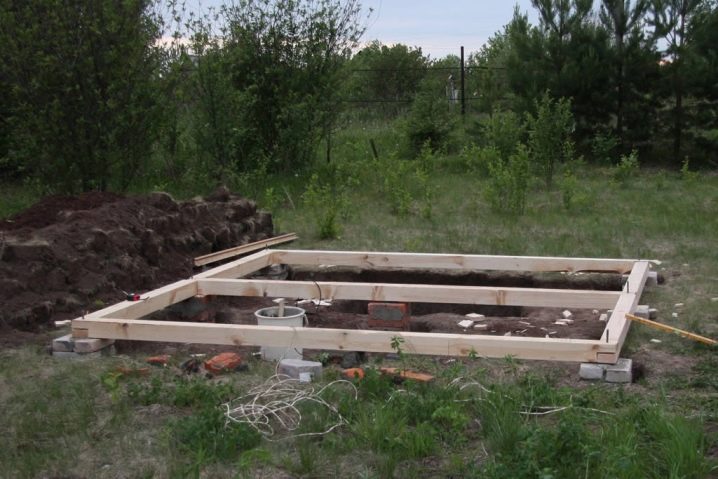
On the bar for wooden greenhouses
Not all acquire ready-made metal frames. For those who collect the frame manually from wood, it is recommended to use the foundation of the same material. Here you can use as a bar with a special impregnation, and sleepers treated with bitumen.
At the corners of the wooden foundation should be installed columns of brick or concrete, so that the design does not subside.
From available materials
The timber can be replaced with old pallets, soaking them with a protective composition. The concrete foundation is well replaced by automobile tires with large pebbles or rubble inside.
Frame
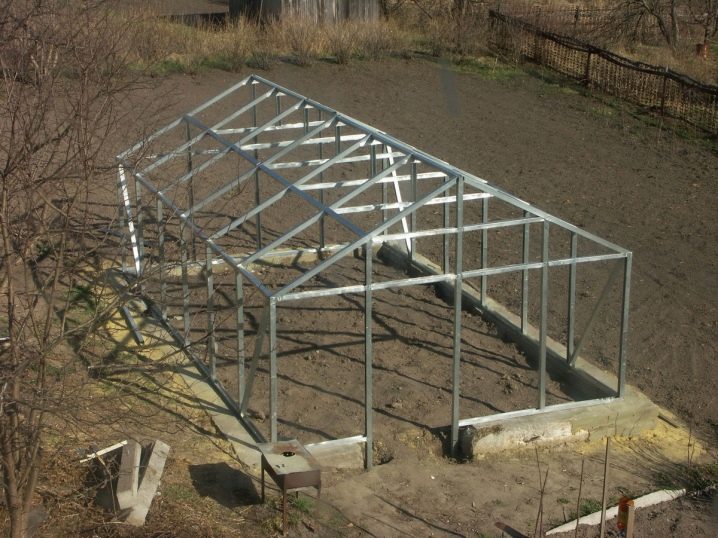
By choosing the basis of the whole structure must be approached wisely. There are two options for choosing a frame: assemble it with your own hands and get it ready.
Given the fact that the production of greenhouse frames of various shapes and heights in our country is well established, the first option loses in all respects.
There are several reasons to choose a finished frame:
- it is a solid, sturdy construction that will last for more than 20 years;
- the manufacturer gives her a guarantee;
- the cost of consumables for the independent production of the frame is equal to the cost of the finished product;
- buying a finished frame saves time and effort;
- production possibilities are wider than when making a carcass independently, for example, to acquire a greenhouse of the desired height and width, so that the inside climate is suitable for plants.
You can independently make a frame of wood, galvanized profile, PVC pipes.
The tree provides more options. A greenhouse will be as tall, wide and shaped as it was intended.
The galvanized profile is more difficult to work with, because tools for metal processing are needed. A steel frame with your own hands and not to make at all without special equipment with which it can be bent, cut and welded.
PVC pipes are easy-to-use material, but it imposes many restrictions. From pipes it is possible to collect only the greenhouse of an arch form and it will lose to other types in durability, stability and service life.
Therefore, the optimal solution is to purchase ready-made frames or factory collapsible greenhouses that can be removed for storage in the cold season.
As for the shape of the greenhouse, it affects both the operation of the building and its aesthetic qualities.
She comes in different forms:
- rectangular;
- polygonal
- pyramidal;
- arched.
Each species has its own characteristics, advantages and disadvantages.
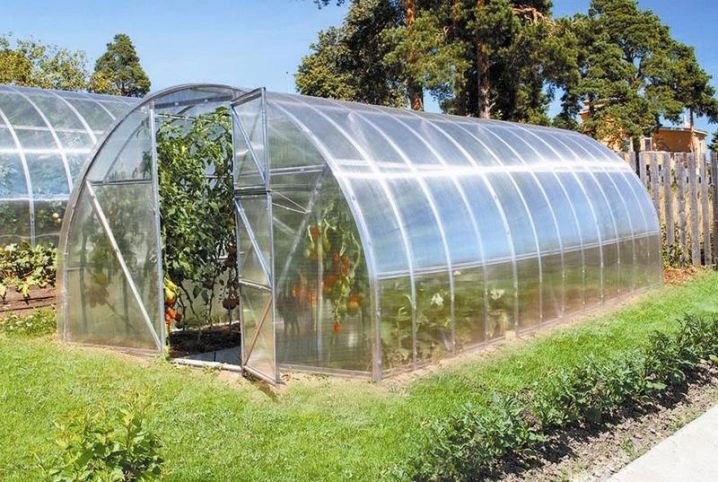
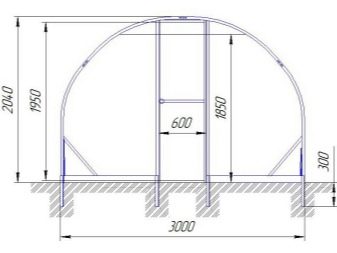
Arched greenhouse is the easiest to install. To mount it, you can use hollow aluminum pipes or PVC pipes. It will be possible to build a greenhouse with your own hands in one day, and you don’t need as much material as a rectangular greenhouse.
But the pluses end there.
The height of such a greenhouse does not allow hot air to rise upwards for a long distance, which is why the plants in it begin to overheat. This reduces the yield.
Work in full growth in such a greenhouse will not work. Its maximum height is about 150-160 cm. This is below the average person height. It will also be problematic to plant tall plants in it, since they have nowhere to reach in close spaces.
Pyramidal greenhouse - a rarity on the site. Gardeners choose it as an experimental sample. Such a greenhouse rarely happens with a foundation, temporary collapsible structures are more suitable.
Pyramidal greenhouses are convenient for experimenting with planting new plants.
Polygonal greenhouses look original and beautiful. In addition, their sophisticated design ensures an even distribution of solar heat and light throughout the day. But to build such a greenhouse is more complicated and more expensive than arched or rectangular.
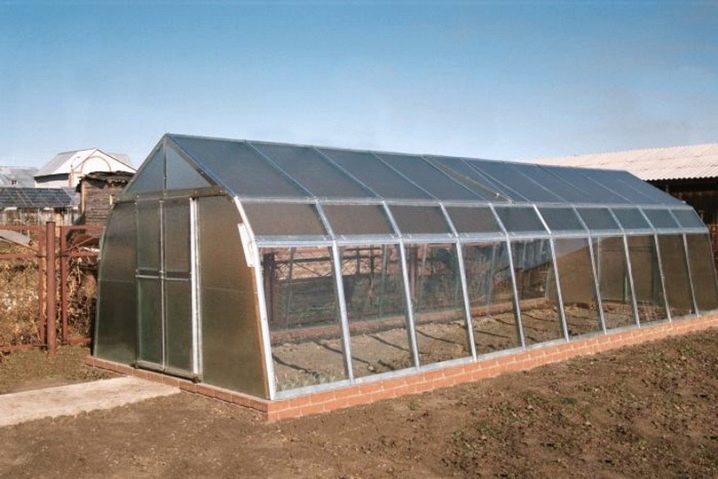
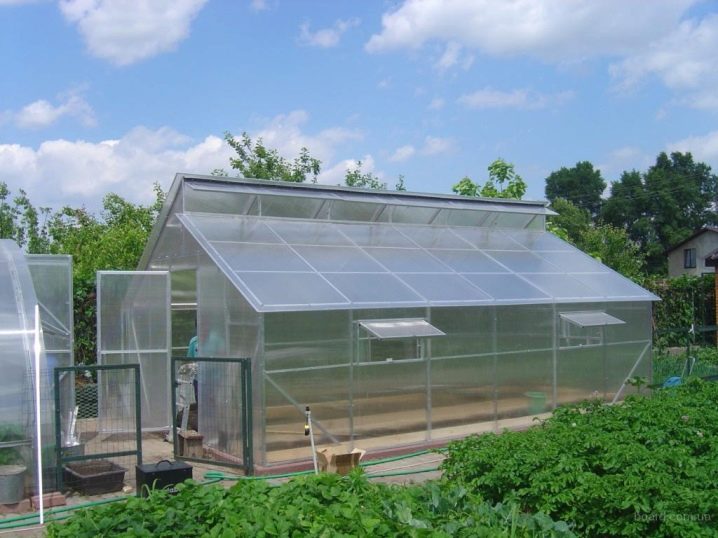
Rectangular construction "house" - the most common and convenient option. It is well illuminated by the sun, it warms evenly, it is convenient to air it.The height of the greenhouse-house is on average 2-2.5 meters, so there is enough space in it so that the warm air goes up, the plants are freely stretched to a height and it was comfortable to work indoors to its full height.
Rarely used greenhouses of unusual forms due to the fact that they are harder to make their own hands and more expensive to buy in finished form. Meanwhile, they are functional and easy to use. Non-standard types of greenhouses include:
"House" with sloping walls
This is a modified for-wall construction of the house, which combines the advantages of a rectangular and arched. Due to the fact that polycarbonate walls are installed with an inclination inward (slightly, degrees 20), there is more space for planting beds. However, the elongated roof of the house provides the removal of hot air upward and free movement inside the building.
It is more convenient to sheat inclined greenhouses with polycarbonate than with glass, because it is flexible and more reliable than with PVC film, because carbonate sheets are stronger.
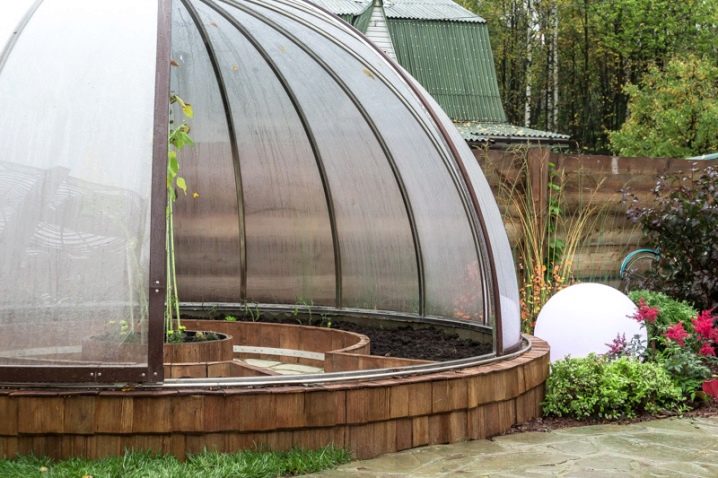
Geodesic dome
Besides the fact that this spherical design looks original on the garden plot, it has enough advantages. Geodesic dome due to the large number of faces in the design catches sunlight throughout the day.Inside it is good ventilation, and the aerodynamic shape helps to protect against strong wind. The design remains intact, despite the low weight.
The disadvantage of such a greenhouse is that it can only be moved if it is large enough.
Greenhouse Mitlayder
The find of an American gardener helped solve the main problem of low greenhouses - poor air circulation. Plants literally disappear and do not breathe. The design feature proposed by Mitlider is that the northern slope of the greenhouse is 30-45 centimeters lower than the southern one and less steep. It connects to the southern slope like a stair. From the side it looks as if two arched greenhouses of different sizes were divided in half and combined the smaller half with the larger one, fastening them with a step above. This step remains unclosed, air is circulated through it.
In the Russian climate, it is recommended to use a modified version. - with closing ventilation. At the first strong frosts, the plants will be damaged due to such an active supply of cold air.
Vegetarian
In essence, it is the same as the wall greenhouse, but it has its own blank wall. It turns out reinforced and reliable design with functional features.
Its main difference is that a reflective material is located on a blank wall. It doubles the sun exposure, which increases the efficiency of the greenhouse at no extra cost.
To mount a vegetarian is more difficult than other types of greenhouses.
Drip
Such a greenhouse is similar in design to the arched, but the central part of the roof is not formed by a smooth arc of a bent polycarbonate sheet, but by the junction of two sheets.
The roof in the construction is inseparable from the walls, because it is one sheet that gently bends from the bottom up to form a streamlined triangle. It does not linger on the roof in winter, and the height allows a person to stand inside the attic in full growth.
Roof
An important factor is the roof structure. They differ in shape and mobility.
Some roofs are stationary, that is, they have no opening mechanism, while others are sliding. They can be opened and closed depending on weather conditions and time of year.
The shape of the roof can be of several types.
- Saw This option is related to the wall greenhouses and vegetarians Ivanova. Since one of the sides is a blank wall, there is no point in a gable roof. Arrangement of one slope simplifies care of the greenhouse in the winter - it does not linger on the snow.
- Gable This is the classic version of the greenhouse "house". The sharper the slope of the slope, the better the snow masses from the polycarbonate sheets slip in winter and less risk of damage to the structure from the severity of raw snow. The roof of the drop greenhouse can also be considered a gable. Although technically it represents a whole with the wall, in the design it serves as a roof.
- Mnogoskatnaya Such greenhouses are more like four, six and octagonal pavilions. Their frame is usually made of wood, and transparent polycarbonate is chosen for plating. The multi-slope roof allows the sun to penetrate evenly inside the greenhouse during the day and does not accumulate snow.
- Attic. Such a roof option implies large dimensions of the greenhouse. Structurally, this is a modified version of the "house", but with a smoother transition from the slope of the roof to the wall.
- Dome. It is peculiar to spherical greenhouses.More often the design is perceived as a single whole, without division into its component parts in the form of walls and roofs.
- Round. Its other name is arched. This is such a greenhouse roof, which is obtained by bending the polycarbonate sheet. One sheet forms both the walls and the upper part of the building at once. Its installation is the easiest, but the possibilities are limited due to the small height.
- Removable. Greenhouses with a removable roof have not yet become widespread, but this is a profitable construction in many respects.
First of all, it will not suffer in winter from a large amount of snow. It will fall inside the building, from where it will be easy to remove it closer to spring.
And the fact that in winter the land will be under the snow is an additional advantage for it. After all, snow is a natural precipitation, and it protects the earth from freezing.
The removable roof also makes it possible to easily carry out ventilation in the greenhouse when the weather is hot.
The type of construction of the foundation and roof is important to choose in accordance with several factors. These include: dimensions and topography of the site, soil moisture and fertility, the type of climate in the region, the types of crops that will grow in the greenhouse. Not in all conditions the same greenhouse will be as efficient as possible.
Dimensions
The dimensions of the greenhouse may be small, medium or large.
The division according to such criteria is rather arbitrary, since it is necessary to take into account three basic parameters: the length, width, and height of the structure.
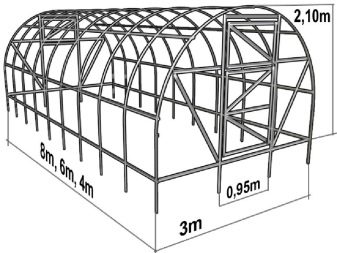
The width of the greenhouse is a decisive factor. It is calculated by the number of beds that can be planted along the parallel. Usually these are two - left and right, for a greenhouse of standard width. A small greenhouse should be at least 180 cm wide. It is important to note that there will be a door in the greenhouse, and the width of the door opening is calculated on the parameters of the average person and is 50-60 cm.
Indicators of 240-340 cm are characteristic for a medium-sized construction. Such greenhouses make it possible to equip a third garden bed in the center of the building.
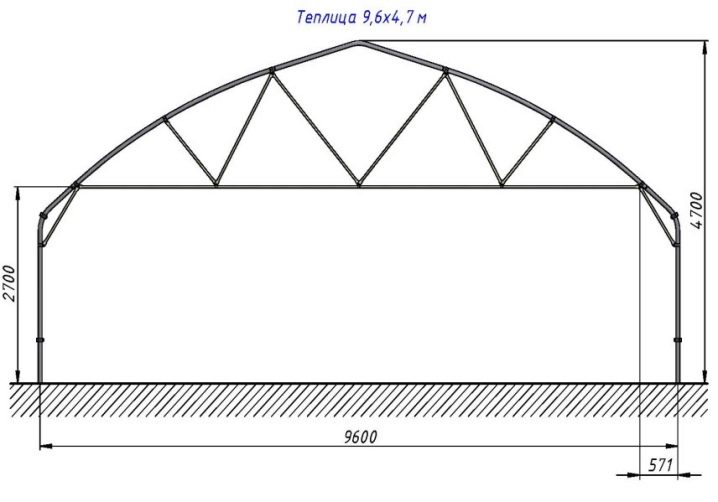
A large greenhouse has a width of 340 to 440 cm. It is possible to fit the largest number of beds and racks in 3 or 4 rows.
Equally important is the height of the structure. In order to not have to work constantly in the greenhouse on a slope, squatting or even on the knees, it must be of such a height that allows you to straighten up to its full height. The minimum value for the height of the object is 160 cm, the average is 200 cm, and the large height is 250 cm.
High greenhouses are more productive, since air circulates better in them and a microclimate that is most suitable for plant growth is created. And working in them for a long time is more convenient.
The height of the greenhouse is determined by the shape and width of the structure. The most convenient in this respect, greenhouses house, drip and mansard.
The length of the greenhouse can be any. The only condition is that it must be a multiple of an even number so that you can pick up the exact number of sheets of polycarbonate without cutting them.
Another landmark is the size of typical pallets for planting greens. This is necessary for those who do not want to form the beds themselves. The length of the greenhouse must exactly fit several pallets. Quantity - at will.
The length of a small greenhouse is only a few meters, medium - 4-6, large - about 10. You should not choose too long construction, because you have to tinker with the arrangement of the foundation and the supply of heating and water.
It is important to bear in mind that the larger the size of the structure, the stronger the frame and the more secure the foundation.
In addition, with the increase in the greenhouse in size, the financial costs of its arrangement and maintenance are growing. This applies to both building materials and systems inside the building: irrigation, heating, ventilation.
Additional materials
The set of materials for the arrangement of the greenhouse, from the foundation to the ventilation, is relatively small. Let's start from the bottom up.
The first thing you need to work, it is alluvial river sand or career sand for sand pillows under the foundation. Then you need sheet material for waterproofing, so that the foundation is not destroyed by groundwater. Suitable dense polymer film with an overlap of 15-20 cm or bituminous paper.
The foundation itself is selected depending on the type of frame. For wooden greenhouses need timber or impregnated sleepers and brick columns. For heavy structures suitable concrete mix of cement, sand and stone, for less weighty, you can use brick and concrete pillars without internal filling space.
For filling of the base cement of brand not lower than M300 is suitable. It is desirable that it is characterized by resistance to moisture and freezing.
Next comes the frame itself. Polycarbonate goes well with all kinds of materials.
If we are talking about self-assembly of the frame, the range for selection is quite large.
- Timber and wood. Wood is convenient for hand-made assembly.The framework will turn out strong and will have good heat-insulating qualities. But do not forget that wood is afraid of a large amount of moisture and does not apply to biostable materials. It can be spoiled by pests and weather conditions, therefore, to protect the frame, the tree is impregnated with special protective compounds.
- PVC pipes and profiles. Lightweight, biostable and ductile material with low thermal conductivity. It is convenient to work with him, but greenhouses from own plastic are not distinguished by high strength and resistance to stress. It should also be borne in mind that plastic is strongly narrowed and expands with temperature differences, therefore, gaps for thermal expansion must be provided in the design. Plastic frame factory production safer and stronger. The manufacturer gives him a warranty of several years.
- Metal carcass. Here galvanized pipes or profiles can be used, for which a special machine is needed to give the construction details the desired shape. More often, when they talk about the metal frame, imply factory workpiece.They are durable, stable, have a long warranty period.
The strength of the frame ensures its proper assembly. A robust design that will sustain the snow mass in winter is done with a profile forming pitch of 50-60 cm. The pitch may be less, but not more.
For sheathing the carcass, flexible sheets of light polycarbonate about 15 mm thick are needed. Cellular polycarbonate is preferred, between the sheets of which are located the edges of cruelty of the vertical and oblique type.
Polycarbonate alone is not enough for plating. In addition to it, you need a sealant for sealing cuts, so that they do not get moisture, and fasteners.
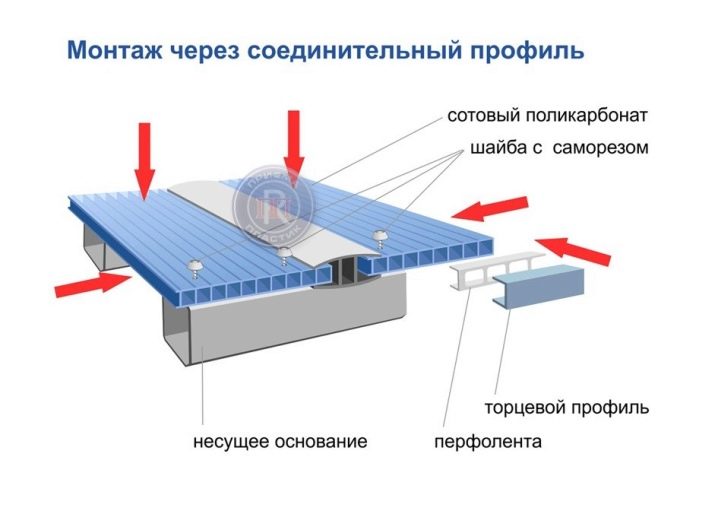
Carbonate is mounted in two ways. For the first you will need a special profile. The carbonate sheet is inserted into the groove, then the profile is attached to the frame with self-tapping screws. With this mount, you need to be careful, because the polycarbonate will expand and taper with temperature changes. If inside the profile it is stitched with a self-tapping screw without a margin for expansion, then in the future a crack may form in this place.
The second method involves the use of so-called "thermal washers" and waterproofing. It is more complicated and more expensive, but more reliable.
For the complete assembly of the structure, you will need more accessories (hinges, handles, opening and closing mechanisms) for arranging doors and air vents.
Some gardeners in the final cover the structure with protective agents to extend the life. It is important not to overdo it, because greenhouse is not important in itself, as a construction, but as a functional building.
It is necessary to choose such protective coatings (films or aerosols) that will not prevent the penetration of sunlight into the greenhouse, to the plants.
Required tools
To prepare for the installation and implementation of the process itself, you may need drawing tools, a tape measure and a building level. They are needed to install guides for self-assembly of the frame and its trim.
That sheets of polycarbonate did not go at random, the first of them should be set as exactly as possible.
For cutting sheets, a circular saw is needed so that the carbonate sheet does not crumble, but is obtained with an even and straight cut. If there is no saw, a sharp construction knife will do.
After the sheet is cut, carbonate chips must be removed from the inside.This can be done with a vacuum cleaner.
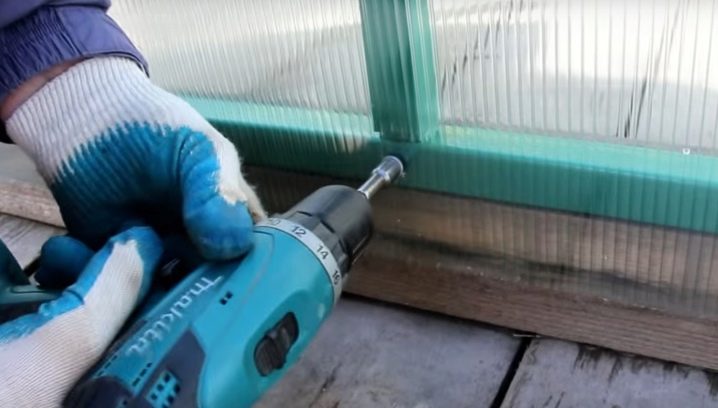
To attach the frame to the foundation, you need a drill and anchor bolts. For the skin of the frame need a screwdriver, because the drill for this has too much power and number of revolutions. It is better to choose a screwdriver wireless and have a spare battery for it, since there will not be enough charge for a full skin of the carcass.
When covering high greenhouses need a steady stepladder. A screwdriver, carpenter's hammer and rubber mallet may be useful. Also, do not forget about the elementary means of protection: gloves, glasses (when cutting sheets), working clothes, comfortable shoes.
How to sheathe?
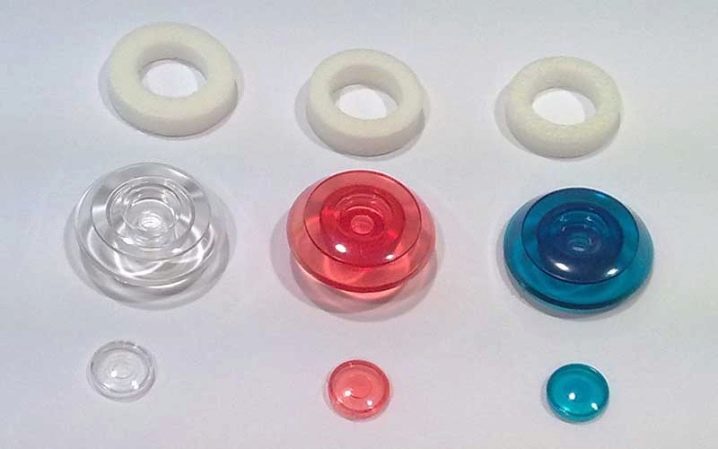
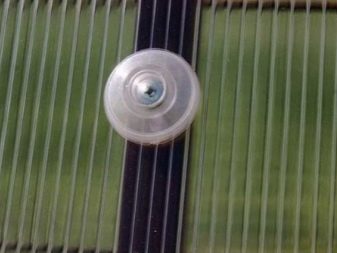
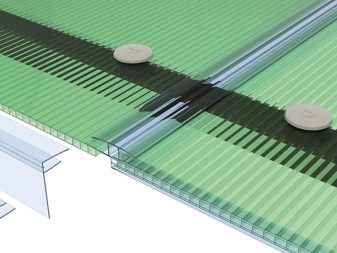
The most reliable type of mounting polycarbonate professional installers recognize mounting on thermo washers. These are the fastening parts, which are a structure made of a sealing ring, a housing and a protective cap. The screw is screwed into a special hole in the center of the case, and the top is closed with a cap.
The “body” of the washer can also be made of rubber. Such washers are more expensive, but more effective. When using them, polycarbonate is protected from cracking in the place where the screw is screwed.There is a gap under the rubber sealing ring, which takes into account the expansion of the material with increasing temperature, and at the same time it does not allow the warm air to go outside through the holes in the mount, and the water to get inside.
Thermal washers produce different diameters, thicknesses and colors. The last parameter is not so important, it is responsible for the aesthetic function, but the diameter should cover the hole in the sheet by a few millimeters. Sealing ring should choose a thickness of not less than a few millimeters.
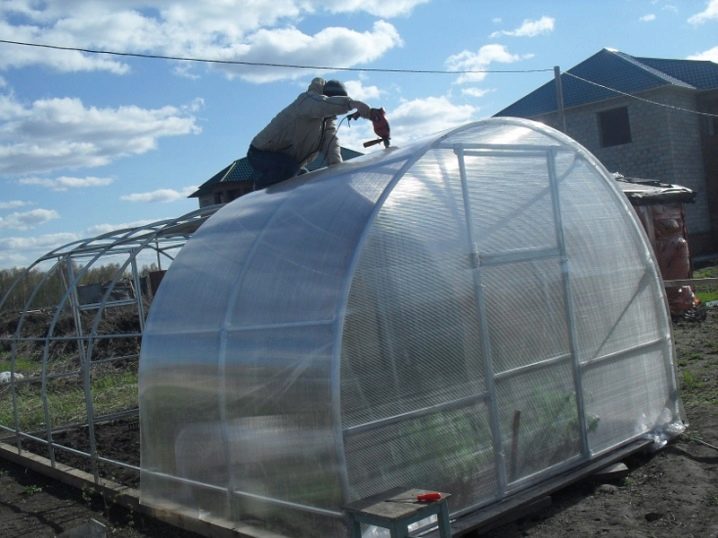
When materials are selected, you can proceed to the trim.
The process is carried out step by step.
- Preparatory work. At this stage it is necessary to check whether the greenhouse housing is in order, whether there are any damages on the polycarbonate sheets. All materials are mounted exceptionally dry in warm and dry weather.
- Cutting sheets. This stage is not always necessary. For example, for an arched greenhouse, it is enough to purchase carbonate sheets of that length, which is necessary for the formation of walls and a roof simultaneously. It will be necessary to tinker with greenhouses of more complex forms, measuring the desired size of the fragments, putting their outlines on a sheet and cutting out with a grinder or construction knife.
- Processing slices. If the polycarbonate sheets are not mounted using a dense profile, in which the sheet fits tightly, then open-honeycomb sections are treated with a sealant. This is necessary so that moisture, dust and insects do not get inside. Liquid sealant can be replaced with tape.
- Markup for holes. Finished fragments for plating are applied to the body. Such work needs to be done at least in four hands, so that the sheets do not move out when marking is applied to them.
- Drilling holes. Screw the screw directly into the sheet and frame - a big mistake. First you need to determine with what step and at what points the fasteners will be fixed. Then drill a hole with a drill with a large-diameter drill bit that will be larger in size than the diameter of the screw. Only then can the sheets be attached to the frame and fixed.
- Sheathing Polycarbonate fragments are mounted alternately with a screwdriver and fasteners. The self-tapping screw needs to be screwed into the body perpendicular to the frame, not diagonally. Each attachment needs to be checked immediately, since the sheet dismantling will take a lot of time, and it will only be used again for minor damage around the holes.
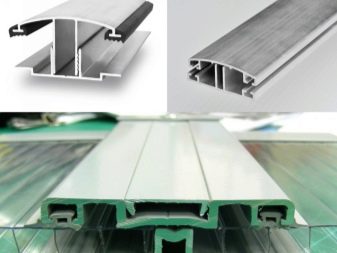
Alternative mounting options - profiles.They are detachable and one-piece, wall, end, ridge and corner. Profiles are used to connect elements of plating, separation and tightness.
Profiles have several advantages: they make it possible to assemble parts of the structure on the ground, and then to connect them around the frame as parts of the designer, fixing them with fixative elements. Replacing them is also easy. When using profiles, there is no need to seal sections with a sealant. They are suitable for plating greenhouses of complex shape, but are not suitable for arched greenhouses.
The disadvantages include the high cost of construction with mounting profiles and complexity in the calculation of parts.
Profiles are made of the same polycarbonate or aluminum.
Internal organization
The greenhouse trim is only half the battle. To use it effectively, it is important to properly equip the space inside: to choose the size and location of the beds, to organize a system of irrigation or water, lighting and heating.
Artificial lighting in the greenhouse is carried out as in any other business premises in the country. The main task is to choose the right type of light bulbs for lighting.
Types of lamps.
- Incandescent lamps. The cheapest, but rapidly becoming obsolete option. Its advantages are pleasant yellow light and low price. They have much more disadvantages: a fragile glass flask that does not withstand temperature and humidity differences in the greenhouse, a short service life, a high degree of heating.
- Halogen. It differs from its previous prototype by a more complex internal structure, therefore it lasts longer, but for greenhouse conditions it is not the best option.
- Fluorescent. Such lamps are also called energy saving. They have a solid body and a convenient form - elongated tubes. They last longer, but emit harmful rays, and mercury vapor is used in their creation. If such a bulb breaks in a greenhouse, the consequences will be unpleasant.
- LED. LED lamp - lighting device of the last generation. Wins in energy efficiency, efficiency, resistance to use in a greenhouse microclimate, long service life. The disadvantage is one, but it pays off over time - the high cost of LEDs.
Choosing a lamp is not all. To make the lighting safe in the greenhouse, where there is constant dampness, you need to take care of high quality wiring insulation.It is best to install protective boxes and install them in the upper part of the walls.
Watering
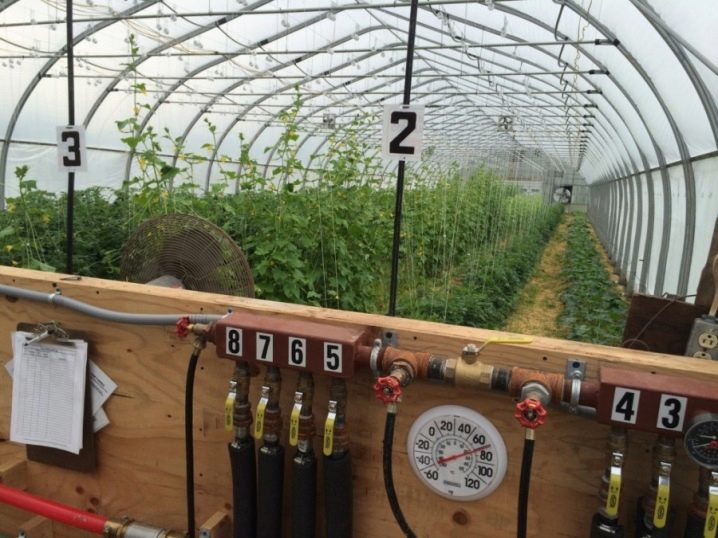
Plant irrigation and watering can be done manually and automatically. For manual irrigation, you need a container with water and a hose with interchangeable nozzles, and for automatic irrigation, a complicated mechanism that only works when necessary. In this case, temperature and climate sensors are installed inside the greenhouse, and when the level of humidity and heat becomes too high, the irrigation mechanism takes effect.
Besides the fact that it simplifies the care of plants, automatic irrigation has other advantages. For example, it is possible to warm the water to a certain temperature at different times of the year or to supply water in individual portions for unpretentious and capricious plants.
Irrigation mechanisms, there are three: “Sprinkling”, subsurface system, drip system.
Sprinkling refers to the easiest ways. It should be considered, rather, semi-automatic due to the nature of the device.
When sprinkling sprayers are mounted above the flower beds, and if necessary to carry out irrigation, they are connected to the hose.Water through the hose goes to the sprayers and irrigation occurs. Gardener's participation is minimized.
The drip system is designed for this type of dachas, where water is supplied once or twice a day at certain hours and it is not possible to use it for watering in unlimited quantities. Water for such a system is stored in a barrel, which must be replenished regularly.
For capricious plants there is a complex soil water supply system. It is a pipe or hose along the beds with drainage systems for each bush. In thin tubes, water is supplied to each plant individually.
Heating
The presence of the heating system is what distinguishes the greenhouse from the greenhouse and makes it possible to start and finish the harvest earlier and later. It is important not to lose the choice of the system.
It can be of several types.
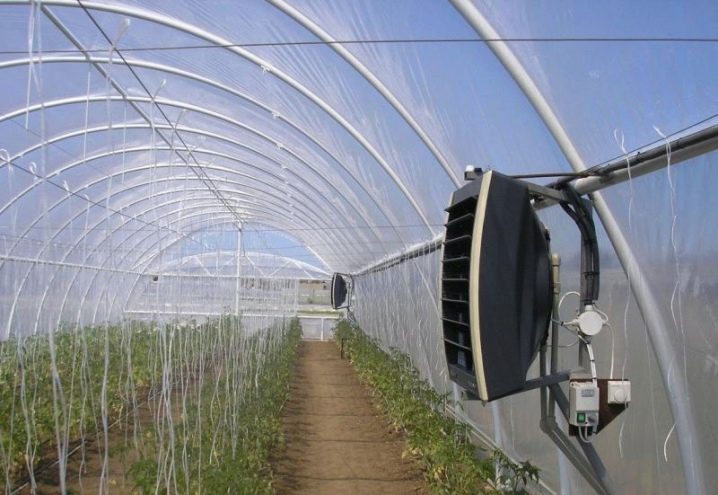
- Air. This is the use of heat pillows in the form of fans, which are mounted through a certain distance inside the greenhouse. They quickly heat the room, maintain the desired temperature and are easily controlled. The temperature can be adjusted as accurately as possible. The disadvantages of air heating arethat the system is dependent on electricity and has significant energy costs. Also, the constant flow of warm air violates the microclimate, drying it.
- Water. This method involves the installation of iron or PVC pipes through which hot water flows. The water system should simply be connected to communications in the house, otherwise it will be expensive and problematic to lay and connect it.
- Gas. Gas heating is cheap and efficient, but unsafe. To install gas pipes in a room that freezes and overheats and where there is active gardening work is a risky undertaking.
- Cable Modern and efficient system, which in its structure resembles a cable heated floor. Heats the soil quickly and evenly, but the energy costs for maintaining the system are too large.
- Radiator. Alternative air heating. As a source of heat are ordinary garden radiators, working on the network. They quickly heat up the room, but consume a lot of energy, and heat is uneven. Near the radiator air will be several degrees warmer than at a distance.
- Infrared The most modern and reliable system.It not only heats the greenhouse well, but also emits long-wave UV rays that are good for plant growth and disinfects the air. The installation of an infrared system is more expensive than any other, but it has the smallest power consumption and a long service life.
When choosing a heating system, it is worthwhile to ensure that the pipes in the ground do not freeze through, the electric wires are not exposed to moisture, and the radiators and fans do not harm the plants.
Tips and tricks
Garden greenhouse will serve for a long time and will delight with a good harvest from year to year, if you correctly approach the choice of materials and type of construction.
Experienced gardeners recommend that you follow several important rules when choosing a suitable greenhouse.
- Choose polycarbonate need a thickness of at least 5 mm. Such material is suitable for arch greenhouses. For structures that do not require maximum sheet flexibility, it is worth choosing a material about 10 mm thick with combined stiffeners.
- Carefully choose a place on the site for the placement of the greenhouse. The most suitable is a plot that is not shaded by trees or shade from a country house, is maximally closed from the wind and does not have large differences in relief.
- Polycarbonate for the greenhouse must have a protective layer against ultraviolet rays.
- Attempting to save on material is obviously a bad idea. High-quality polycarbonate can not be cheap. Cheap goods - a fake, which will become worthless in one season.
- Always build a greenhouse on the foundation. Beginners-gardeners are often tempted to install the frame directly into the ground. This should not be done, otherwise the greenhouse will not survive the first winter.
- Always treat sections with hermetic tape or mortar.
- Do not screw in screws without thermal washers.
- To accurately determine the size of the hole for the screwdriver with an expansion margin, it is necessary to sheathe the body with polycarbonate at a temperature of +10 degrees. At this time, the material is in its natural state.
- Ventilation in the upper part of the structure should be provided in the greenhouse.
- Acquire materials from reputable manufacturers who can confirm the quality of the goods by customer reviews and relevant certificates.
How to care?
Caring for a greenhouse is important because it affects both its efficiency and its service life.
First of all, care measures concern the appearance of the building. By the end of the garden season, dust and dirt from inside and outside accumulate on the polycarbonate greenhouse.It is recommended to remove it not only in order for the greenhouse to have a neat appearance, but also for the sunlight to pass unhindered inside the building.
The top layer of polycarbonate does not tolerate the aggressive effects of alkaline and abrasive materials. They can not be used when washing the structure.
Scratches and stains will remain on the surface.
In winter, the main concern of a good gardener is to prevent snow masses and ice from accumulating on the roof of the greenhouse. Their weight is very large, it can damage polycarbonate. To reduce snow problems, it is recommended to choose greenhouses with a steep slope of the roof or a streamlined shape. If the roof of the building is flat or arched, then it should be regularly cleaned of snow masses.
Reviews
Testimonials from experienced and novice gardeners are mostly in favor of polycarbonate greenhouses. Among the merits they note the opportunity to start planting seeds and greens earlier, increasing yields. The hostesses are pleased that when there is a greenhouse, work with the beds becomes less, because the land inside can be prepared in the autumn, and in the spring to plant the seedlings at a convenient time.
The advantages include simplicity of the assembly of the structure and low prices for finished greenhouse frames.
The classic greenhouse "house" is recognized by most of the most resistant to weather conditions and harsh wintering without special care.
There is also a negative share of reviews. As a rule, these are complaints of masters, whose works on the cladding did not withstand the load of snow and wind in winter.
Beautiful examples
A good gardener will not allow himself to build a seemingly greenhouse on the plot. Hide this building behind the house or in the thickets of trees does not work, it should be in the most open and lighted place. It remains to choose a beautiful design for it.
In order for a greenhouse to serve not only a practical, but also a decorative purpose, it must harmoniously fit into the landscape design of the garden plot. This means that you need to choose the design style of the greenhouse in accordance with the style of a country house or plot.
If the garden belongs to one of the classic options, it is recommended to use simple and clear symmetrical shapes and polycarbonate of reserved colors.
Suitable transparent, pastel, green. For more modern sites need geometric shapes, sharp corners, functionality and transparency. For example, it is possible to make inclined walls a pronounced structural element.
For houses in the style of country, Provence or rustic style are suitable warm and bright colors in the design. You can use pictures on the walls, windows and roofs of unusual shapes, plant flowers nearby.
It is possible to combine the greenhouse in one ensemble with other buildings by using polycarbonate as the roof of the gazebo, veranda, summer house.
For information on how to self-assemble polycarbonate greenhouses, see the video below.