Greenhouse size: what influences the choice?
For the summer residents of most of Russia, the use of greenhouses is a forced measure. Weather and climatic conditions do not allow growing thermophilic vegetables in open ground. Under similar circumstances, a good harvest of peppers, eggplants and tomatoes can be obtained only in greenhouses. The sizes of greenhouses are different. But before the construction of the structure on the site, it is important to understand what influences the choice of a particular size.
Features and selection criteria
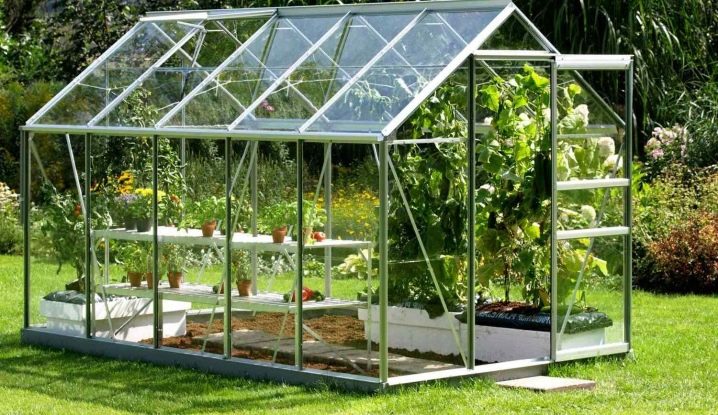
For home gardens, greenhouses are selected according to two criteria. First of all, the needs of the family are taken into account. Large families will suit dimensional greenhouse, for example, 8 meters in length. Requests of a family of two will satisfy a shorter structure - 4 m.
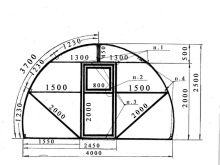
As for the width, then it should be chosen not arbitrary, but quite definite.The width of the greenhouse should be such that it could be equipped with beds and paths. If your choice falls on a structure 2 meters wide, then the center row will pass, and the beds will be located on both sides of it. The maximum width of the bed should be convenient for weeding and loosening. As a rule, eighty centimeters is enough.
In a greenhouse with a width of 3 meters, it is advisable to make three beds and two aisles. The distance between adjacent beds should allow to move freely with watering cans, if not equipped with stationary watering. In addition, it is worth considering that you will not only have to walk between the plants, but also squat and bend over to loosen the ground, weed weed and gather ripe fruit.
The second criterion is free space. For a greenhouse, not just a plot, for example, 3 by 6 meters, is suitable, but a place where:
- there are no fruit trees nearby;
- the long sides of the structure will face south and north;
- the shadow of the house (garage or other tall buildings) will not fall on the greenhouse;
- convenient to bring (bring) water and fertilizers;
- greenhouse will not interfere with the neighbors.
Place to choose in advance.If when marking the territory, for example, under the four-meter structure there is free space, do not leave it empty. It is better to buy a greenhouse with a length of 5 m, and plant in it not only peppers and tomatoes, but a few more eggplant bushes. And remember that the greenhouse must be set so that the plants in it receive the maximum sunlight.
The choice of length also depends on the method of planting. When it is planned to grow not on ridges, but in special pallets or on racks, the parameters of the greenhouse already depend on the available trays and pallets.
The height is selected depending on the height of the plants and the height of the users. A person should be comfortable inside the building. In household structures, as a rule, a height of 2.0 - 2.5 m is sufficient. Industrial greenhouses have different dimensions.
Standard and optimal parameters
Greenhouses produce standard and to order. In principle, the structure can be given any size. However, the choice offered by the manufacturers is so great, so you can always find the right dimensions. So, for industrial production of agricultural products, greenhouses of large sizes with a useful area of several hectares are produced.
Small farms prefer to install several medium-sized greenhouses, for example, per 100 sq. M. These types are standard, they have parameters: 20 m in length and 5 m in width. There are rectangular models measuring 50 by 10 meters.
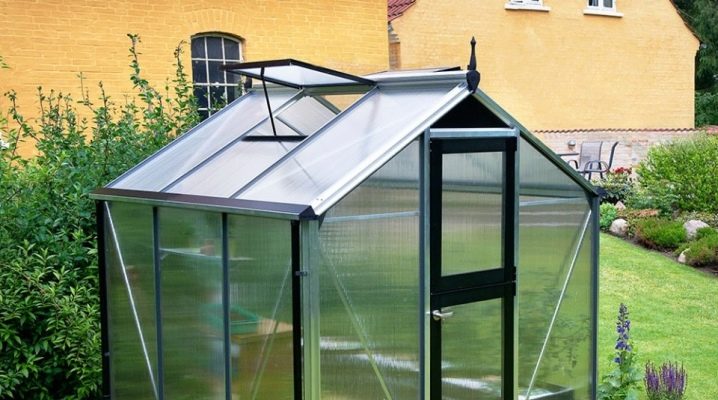
Household designs differ in the fact that their sizes are more compact. In a small area you can install a standard greenhouse with parameters of 3x4 meters. As a rule, this design has a wide doorway, allowing you to easily go inside with the inventory. Two vents are provided for ventilation. In longer models - 3x6 m windows may be larger.
If short greenhouses usually have one door, then designs with parameters 4x6 and 6x3 are equipped with two doors at both ends. In this case, the entrances are with one or two doors. Single doors are installed on arched greenhouses. Bicuspid entrances are sometimes found on a hut-like wide gable model. The more attractive a greenhouse has, the more expensive it is.
The relationship with the components
The forms of greenhouses, to a large extent, depend on the material from which they are mounted.The greatest value falls on the cladding material.
It is known that the walls and the roof should pass light well and reliably protect plants from rain, wind, hail and cold. The first requirement is the power of glass, plastic film and polycarbonate.
Glass is expensive. Installation of glass greenhouses is quite problematic compared to other types of coverage. In addition, the lack of glass is its fragility. Glass can be damaged during spring tillage. It is not insured against destruction by blows of large hail.
Glazing is performed on a metal or wooden frame. Fastening requires additional efforts and materials.
The film is more convenient to mount on a wooden base. Polyethylene is inexpensive, but durability is not different. All that the material is capable of is service during one summer season.
Film shelter can not be called reliable because of the instability to mechanical loads. Any scratch can damage delicate material. Under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, temperature drops and humidity, the film loses its elasticity. Strong wind is able to pull it from the attachment point.You can restore the torn coating only for a short time.
The most suitable material for facing greenhouses today is polycarbonate.
It has undeniable merits:
- low weight;
- ease of installation;
- resistant to sunlight;
- transparency;
- relative strength;
- durability;
- democratic price.
In greenhouses made of polycarbonate, heat is perfectly retained. Due to the fact that polycarbonate sheets bend well, they are ideal for greenhouses with an arch roof.
Arched structures are recognized as the most practical. Rainwater does not accumulate on the surface of greenhouses. Pollution is easily washed off. The cellular structure does not collapse under the influence of precipitation, is not afraid of frost.
Rapid assembly of the structure is ensured by the large size of standard sheets. (2.1 x 6 or 2.1 x 12 meters). Sheet thickness for greenhouses is 6 - 8 mm. The minimum number of joints reduces the work on their sealing. Despite their large size, sheets are easy to transport, as they are easily rolled into a roll. Polycarbonate is cut with a regular knife.
Frame material and foundation
The durability and strength of the product depend on the material of the frame. The main source components for the skeleton of greenhouses are wood and metal.
The tree has been used as a building material since ancient times. Not abandoned him in our days.
Wood products have a lot of advantages:
- ecological cleanliness;
- low cost;
- ease of processing;
- light weight and ease of installation.
The disadvantage of wood is a predisposition to rotting at high humidity. The framework has to be regularly treated with antiseptic agents. But at the same time the wooden frame will serve for several years.
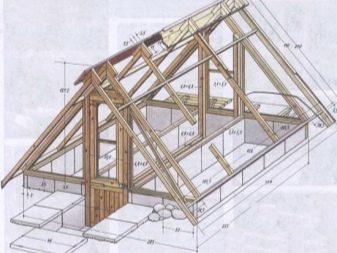
Greenhouses are made from greenhouses with one or two ramps. It is possible to make the roof in the form of an arch, but the costs will be unjustified, therefore other materials are used for the semicircular roof.
Very often, greenhouses are made of metal. Frameworks are very durable, able to withstand heavy loads. The service life of metal frames significantly exceeds the wooden counterparts.
Supports are usually made of lightweight aluminum tubes. True, non-ferrous metal is more expensive than, for example, galvanized steel profile.
The pipes are easy to bend, give them the shape of an arch. Aluminum, unlike steel, does not require painting or other surface treatment. It does not rust, does not rot, is resistant to temperature changes, does not collapse under sunlight.
In addition to the relatively high cost of aluminum, there is another drawback - poor weldability. At home, perform welding work will not succeed. Ready-made designs of standard sizes are available. If the dimensions suit, then this is the best option.
A greenhouse is a light structure. Despite this, she still needs a foundation. A greenhouse without a good foundation cannot stand in place under strong gusts of wind. The foundation also allows for better heat retention within the building.
Reliable base extends the life of the whole structure. Perhaps the most suitable option would be a strip foundation of a small depth. Do not do without a capital foundation when using greenhouses all year round.
If the greenhouse is designed for growing vegetables in the summer, you can get by with a simple option - a superficial one.
The material for the foundation are:
- concrete pouring;
- reinforced concrete blocks;
- Red brick;
- wooden bars treated with a means of rotting.
The choice of material affects the appearance of the greenhouse, plant comfort, quality and quantity of the crop. The material must be selected according to the type of coating. For example, glass requires a more rigid foundation than polycarbonate.
Greenhouse shape
The shape of greenhouses varies in:
- height;
- foundation form;
- view of the roof.
The height of the structure depends on the "growth" of the grown crops. Width and length - from the needs of the owner of the site and the territorial possibilities.
The most popular is the greenhouse arch type. The design allows you to grow both stunted and tall plants. It is assembled from separate sections. By adding or subtracting sections, the length of the structure is regulated. Ideal for polycarbonate.
Greenhouses with a lean-to roof are usually attached to some kind of capital structure. They are located either from the south or from the west side of the building in order to stay in the zone of direct sunlight as long as possible.
Cover the attached greenhouses with glass, as it is better than other materials transmits light.For growing seedlings of flower and vegetable crops, models with a single-sided roof are used.
Gable models are more often odnoskatnyh. Placed facilities in open space. Coating can be a film, and glass, and polycarbonate. A variation of the gable greenhouse is the Dutch. Its difference from the classic dvuskatka is that the sidewalls are not vertically, but obliquely.
Pyramidal and tent greenhouses are rare. Both types are compact, installed in small areas. You can grow seedlings, herbs, flowers in such facilities.
Polycarbonate greenhouse installation
Before the installation of the greenhouse, you need to prepare and mark the plot. Pegs are set up on the territory designated for construction. Along the perimeter of the future greenhouse should dig a trench. The bottom of the trench should be leveled and trampled, and the horizontal should be checked at the building level. Only small drops are allowed.
Otherwise, the structure is threatened with distortions, which is highly undesirable. Alignment has to be done by adding sand (earth) or lining bricks, and this requires additional time and physical effort.
The trench is laid out or poured foundation. The role of the foundation can play a wooden beam laid on a gravel-sand pillow or brick supports. Installation on the outer edge of a trench of old flat slate will be useful. It will prevent the penetration of weeds to cultivated plants.
All purchased greenhouses are supplied with assembly instructions. If you follow the manufacturer's instructions, focusing on the figure, it is not difficult to assemble a greenhouse. For work, you need a simple tool and an assistant.
In simplified form, the assembly consists in:
- arrangement of the base;
- lower strapping assembly and its attachment to the base;
- exhibiting racks-arches;
- fastening racks;
- cutting and fixing polycarbonate along the ends of the greenhouse to the frame (including making cuts for doors and air vents);
- installing and securing end parts;
- covering of arches with sheets of polycarbonate;
- fixing polycarbonate sheets to the arcs with metal clips.
A few hours later the greenhouse is fully prepared. It remains only to dig up the ridge and plant the grown seedlings.
How to choose a greenhouse, see the next video.