Warm beds in the greenhouse: step by step production
Winter is a sad time for an amateur gardener. He counts the days before the long-awaited time of cultivating the land and planting vegetables and fruits. But there is a way to reduce the waiting time of the planting season - this is the arrangement of warm beds in your greenhouse, which can bring the time of your favorite activity closer.
Features and benefits
Warm beds are a simple structure that maintains heat in the root layer of soil. Due to this, the plants develop and bear fruit faster than in ordinary soil. And the availability of materials and ease of manufacture of such beds allow you to use this method to any gardener.
If we are talking about greenhouses, which, according to the logic of things, should be warm, so why equip these facilities there. In spring, the soil warms up slowly enough.And the optimum temperature for planting seedlings is reached only by the middle of spring. If the soil is already heated, then the planting can be done much earlier, at the very beginning of spring. At the same time, plants feel comfortable, take root and develop faster. The heat from the beds also warms the air in the greenhouses, the optimum temperature is reached, a suitable microclimate is created for the healthy growth and development of the seedlings.
Benefits
Warm beds have many advantages compared to planting plants in the ground.
- relatively early planting of seedlings, so you can get a crop by the beginning of summer;
- rarer feedings;
- long period of fruiting;
- fewer weeds;
- resistance to unexpected frosts;
- beauty of the design of beds and ease of care for plants.
How to build yourself?
Selection of materials
The choice of materials for creating warm beds is large enough. If we are talking about the design of the box, then everything is limited only by the fantasy of an amateur gardener. It is possible not even to spend money on materials, but just to look into the pantry or shed, there are often stored materials that will be useful for the manufacture of boxes.Boards can be made of wood, plastic panels, metal, polycarbonate, slate, and even plastic bottles. The most popular is several options.
- The sides of the tree. If the tree is not treated with anything, then such a bed will not last long, just a couple of years. Therefore, it is better to treat the wood with an antiseptic in several layers.
- Bricks from bricks. Made of brick, they are very durable, comfortable and will last for many years. But we must not forget that the process of creating a brick fence is quite laborious and requires at least a basic knowledge of masonry.
- Slate sides. Slate rather widespread construction material since Soviet times. With it, you can also organize boards for a warm bed. But it is believed that the broken off parts of slate emit harmful substances to health. This should be taken into account, and try to use only whole sheets.
Device options
There are three main types of warm beds.
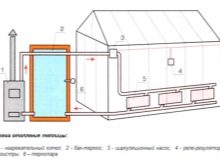
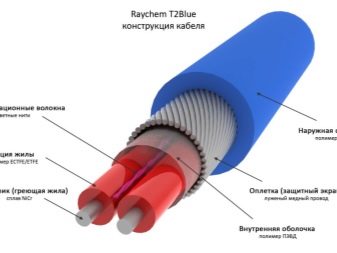
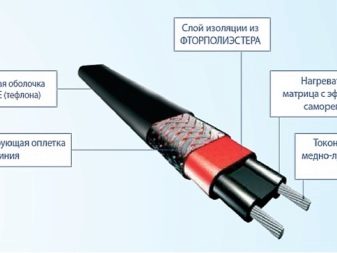
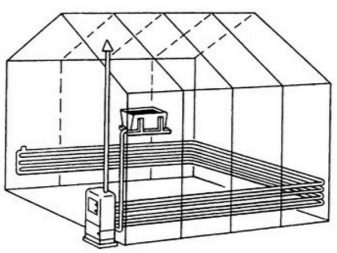
- Electric warm beds. They are based on electric heating cable or tape, which are laid on the bottom of the bed.It is also possible to install a thermostat with which the optimum temperature for heating the soil will be maintained. This is a relatively new way to heat the soil, but many gardeners have already begun to use it. With this method it is important to take into account additional expenses for electricity, especially in the period of cold weather, when heating should be round-the-clock, and for the purchase of necessary materials. If in the region of residence electricity is quite expensive, it is better to prefer another way.
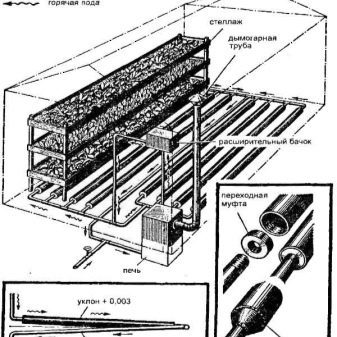
- Water warm beds. They represent the same idea as electrical ones, but the heating elements are pipes, preferably metal, laid on the bottom of the bed. This type of heating will support not only the warming up of the earth, but also provide additional root moistening of plants. It will be necessary to additionally install a stove for heating water and a pump for its circulation.
- Organic warm beds. For the manufacture of such beds do not even need to make cash expenditures. For heating, you can use only biological elements: small wood, leaves, compost, dry grass, and even the cleaning of vegetables and fruits.This is the most economical and easiest way to perform. No need to think that these beds are short-lived. If they are properly formed, then they will serve at least five years. And recycled organic matter will become the ideal nutrient soil for new beds.
Among amateur gardeners, the most common method is biological. It is less labor intensive, simple to perform, durable and economical. With its help, you can also organize spectacular flowerbeds, which will become the pride of the garden from early spring to late autumn.
Required calculations
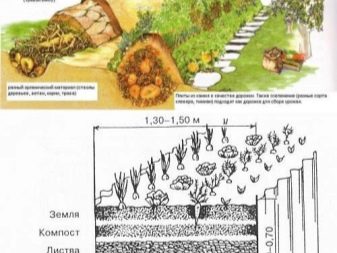
All three types of warm beds are made according to a general principle. The first step is to draw a diagram of your greenhouse and decide in which places the beds will be located. Based on the area of the greenhouse, you can calculate the length and width of the ridge for a more compact placement. Typically, structures are placed along the walls of the greenhouse, leaving a through passage in the middle. You can also form them in the form of the letter "P", or in three rows, if the area of the greenhouse allows.
Electrical heating and heating with water pipes requires additional calculations to purchase the necessary materials.Based on the length and number of beds, it is necessary to calculate how many pipes and electrical wires will be needed.
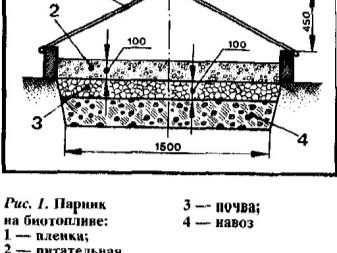
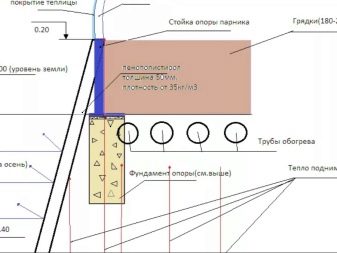
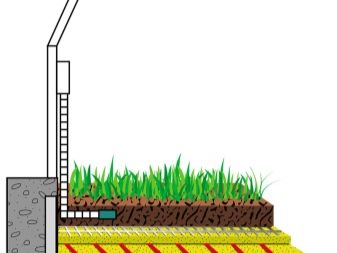
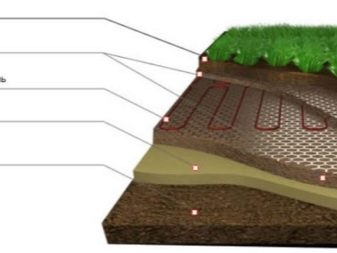
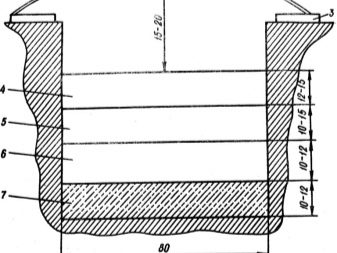
After determining the location of the warm beds, you should calculate the amount of materials needed, and then proceed directly to their production. It is necessary to dig a trench 40–70 cm deep. Lay the bottom with thermal insulating material (polystyrene foam, polystyrene foam and even ordinary plastic bottles), which will prevent heat loss deep into the ground. Then fill the layer of sand with a thickness of 3-5 cm. On it to put a fine metal mesh, which will protect against the penetration of rodents. Then the main heating element is laid (electric cable, water pipes or organic components).
On top you need to create another sand cushionand, finally, to form a layer of fertile soil in which the plants will be planted. It should not be too thick, otherwise it will not be provided with a good warm-up. If the production takes place before winter, it is better if the warm beds are covered with film material.This will prevent the soil from freezing in the cold winter period.
It is also necessary to take into account the general rules on the size of the beds.
- The most optimal height is 30–40 cm. This is the optimal level for weeding and watering.
- Width is better to choose up to 1.2 m. If the beds are wider, the care of plants will be extremely uncomfortable.
- The width of the passage between the beds should not be less than 0.6 m.
Detailed construction instructions
Each gardener has the right to choose the most suitable kind of warm beds, based on their finances, interests and principles. Therefore, it would be advisable to describe each structure in more detail for easy manufacture by hand.
Electric warm beds
This view is convenient due to the ability to independently set the temperature and heating mode. To do this, you only need to additionally install and configure the thermostat. To equip a warm bed using a heating cable, you need to have a basic knowledge of electricity.
They are divided into two types: resistive and self-regulating.
- Resistive differ in that they are not automated, heating of the soil can be uneven. At cost, they are cheaper, but the cost of electricity is more expensive.
- Self-regulating have a thermostat with which you can set the heating temperature and mode. They are more expensive than resistive ones, but they are cheaper in the farm because they consume less electricity.
Consideration should be given to arranging warm beds using a heating cable.
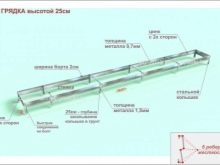
- The first step is to dig a trench 40–60 cm deep, 50 cm wide. The length will depend on the size of the greenhouse. It is necessary to tamp the soil on the sides and at the bottom of the trench.
- Next, the bottom is covered with a thermal insulation coating that prevents heat loss. Styrofoam is ideal.
- A layer of sand about 5 cm thick is formed on top, it will perform drainage functions.
- Then you need to lay a fine metal mesh. A cable will be attached to it, and it will also protect against the penetration of rodents to the roots of plants.
- A heating cable is attached to the grid, it is best to lay it with a snake in increments of about 15 cm, starting from the thermostat.
- Next, a sand pad is formed again. It should be well pushed and shed water.
- The next stage is the safety net. It can be metal or plastic.Its role is to protect the cable from mechanical damage in the process of planting and caring for plants.
- The final layer is a layer of fertile soil not less than 30–40 cm thick. Plant seedlings will be planted directly into it.
- The thermostat sensor is best placed in a corrugated pipe, and the thermostat itself in a moisture-resistant box, and place it at a level of 1 m above the ground.
A warm bed with a heating cable is ready! It is possible to plant plants in it in March. The main time of her work can be considered spring until May, inclusive, when the warm weather has not yet been established and night frosts are possible. Plants during this period just need constant warmth. Also, maintaining heat may be needed in the fall to extend the harvest period.
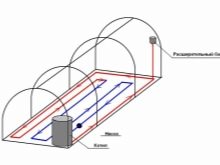
Water warm beds
In this form, heating takes place with the help of pipes in which there is hot water. Pipes are better to use metal, since they give off more heat than plastic. It is also better to choose pipes of smaller diameter and arrange them evenly in a trench for more complete heating of the soil.For heating water, you can use a gas or electric boiler, cast iron or stone stove with wood. For them it is necessary to prepare a stone or brick foundation, as well as equip the chimney. Be sure not to forget about the installation of a water pump. It will ensure the continuous circulation of water in the heating system.
The order of formation of a warm water bed is almost identical to the previous one:
- a trench is dug about half a meter deep;
- heat-insulating material (for example, foam plastic) is laid down;
- then an air cushion is created from a layer of sand 5 cm thick, is well crushed and sheds water;
- then the heating element itself is laid, in this case the pipes through which warm water will flow;
- It is also possible to use a grid as the next layer, which will protect against damage and penetration of rodents;
- The bed is completed by a layer of fertile land for planting.
It is worth considering that with this method of equipment of warm beds it will warm up not only the soil, but also the air in the greenhouse. Thus, plants are provided doubly comfortable conditions.
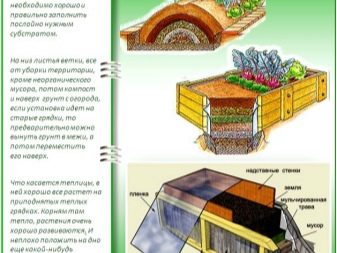
Organic warm beds
This is the easiest, cheapest and most common way of arranging warm beds. There is no need to buy expensive materials, hire people who can competently install everything, pay additional expenses for electricity or water. In this case, everything is much simpler. Only organic waste that is available at each site is needed; waste from livestock can also be used.
There are four subspecies of organic warm beds:
- raised;
- in-depth;
- warm beds, hills;
- combined.
Special features
Each subspecies has its own characteristics.
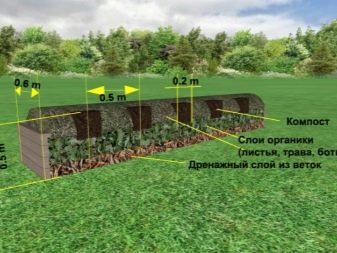
To make in-depth warm beds, you must perform the following steps:
- a deep trench is dug under them, its edges should be flush with the ground level in the greenhouse;
- at the bottom you can pour a layer of sand, which will play the role of drainage;
- be sure to lay a fine mesh, protection from rodents;
- The next layer is empty plastic bottles with tightly screwed caps. They are a heat-insulating layer;
- side walls of the trench can be covered with several layers of thick plastic film or cardboard to maintain heat;
- large wood, branches should be put on the bottles;
- then comes a layer of newspapers or paper;
- then a layer of small wood waste is laid;
- a layer of chopped tops, weeds;
- the next layer of leaves and grass;
- fertile soil layer to which compost can be added.
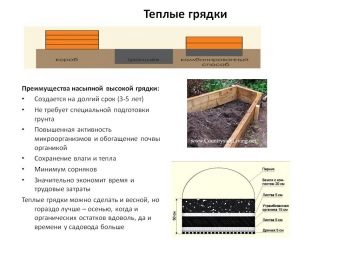
Raised warm beds also differ in manufacturing technology. Under them do not need to dig a trench. They are formed in a box that is pre-made from wood, slate or plastic panels. It is worth considering that the boxes, made of wood, must be treated with an antiseptic solution in several layers in order to prolong their service life.
The main manufacturing steps include:
- the bottom and walls of the box can be made through a thick plastic wrap. You can fix it on the outside either with an economic stapler, or to nail it with strips along the perimeter of the box;
- large wood waste is laid on the bottom, then a newspaper and cardboard;
- the next layer consists of weeds, peeling vegetables and fruits;
- further used foliage, tops, grass;
- the final layer consists of fertile soil;
- the box is installed on a prepared place in the greenhouse;
- it is better if the opposite long walls of the duct will be connected by transverse beams, which will prevent the structure from creeping under the pressure of the soil.
Warm beds, hills - this is the easiest option to perform, as it implies the least effort. There is no need to dig a deep trench or make a special box.
The manufacturing process is as follows:
- the first step is to mark the plot in the greenhouse under the garden-hill;
- one should dig a shallow trench, about the depth of a spade;
- fill the trench with the necessary organic material in the same sequence as in the previous subspecies, but leaving a little empty space from the edges of the trench;
- voids fill with fertile soil;
- the upper and side parts are also covered with fertile soil;
- the bed will be quite wide (more than one meter), therefore it is undesirable to locate it close to the walls of the greenhouse.
The combined warm beds unite in themselves the raised and deep warm bed.
The manufacturing process includes the following steps:
- not too deep trench is dug out;
- on the bottom of the insulating material is placed, fine mesh;
- large waste of wood is placed, then newspapers or cardboard;
- a layer of small chips, household organic waste, then grass and compost;
- a layer of fertile soil;
- a duct is installed on the surface that will resist the spreading of the soil.
Operating rules
Among all the ways of organizing warm beds, each gardener chooses for himself the best option in accordance with the climatic conditions and the type of soil. These conditions are more likely to influence the way a warm garden is organized. In wet, marshy ground conditions it is recommended to build raised warm beds. They protect the root system of plants from excessive moisture and disease. In a normal warm climate, it is better to build in-depth warm beds due to the fact that there is no need to protect the roots of plants from excessive moisture. In cold conditions it is better to use combined warm beds.
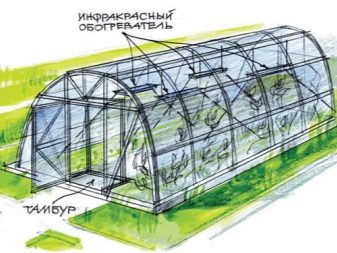
In the coldest months, when greenhouses have not yet been heated by hot sunshine, it is recommended to use electric heaters additionally, they will maintain a comfortable temperature for plants above ground level. Also in country greenhouses used ultraviolet heaters.
Opinion of the owners
If you look at the reviews of the owners of warm beds, you can see a really bright picture. A greater number of authors argue that growing seedlings in warm beds, and even in greenhouses, only in the best way affects the yield. Those who use organic warm beds, argue that in any climatic conditions, the yield increases several times. Note the simplicity of the formation of such beds, the possibility of early planting of seedlings and, accordingly, an earlier harvest. Also, many point to the efficiency and durability of this method. At any site there are always ingredients to create this type of beds. And even a woman can build it with her own hands.
Owners of electric warm beds indicate ease of installation, if you precisely follow the instructions, and the durability of such a structure. Of the minuses emit only the fact that not everywhere in the shops you can find such a system. Some users order kits for installation over the Internet. Marked increased yields, early ripening of fruits and full automation of this method, if you install the thermostat.
Many gardeners prefer a water way of heating the beds. Of the advantages, in addition to high yields and early ripening, they highlight the possibility of self-assembly of this type of heating. Any man is able to install pipes of the desired size and diameter, connect a water pump and put the stove to heat the water. In addition, this method, as the authors note, is more economical than electrically heated beds.
Useful tips
So that the process of growing plants in this way in greenhouses would bring only good results You can use the following helpful tips.
- In the manufacture of organic ridges can not use the affected materials, as this can lead to infection, disease and death of plants.
- You can not lay perennial weeds, as they can germinate.
- To speed up the processes of decay, it would be nice to use biologically active drugs.
- After making the beds you need to shed it with plenty of water.
- Biological warm beds can serve from 5 to 8 years before complete rotting of components.In the future, fertile soil can be used to fill this bed.
- In the first year of use in warm beds the greatest concentration of nutrients is contained, therefore at this time it is better to plant naughty and demanding types of plants, such as cucumbers, cabbage, tomatoes, peppers. In subsequent years, the amount of nutrients decreases, so it is more expedient to plant less demanding, unpretentious cultures. For example, greens, salads, peas.
- High beds require abundant and frequent watering when compared with in-depth options.
- It is necessary to constantly monitor the temperature in the greenhouse to avoid overheating of the plants. It is also additionally advisable to ventilate the greenhouse to improve air circulation in it.
- The optimum temperature for plants in the greenhouse is from +17 to +25 degrees. It is necessary to maintain it throughout the entire process of plant growth and fruiting.
- Electric warm beds require more watering, as the land dries faster, so you need to constantly monitor the soil moisture.
- Heated beds of water pipes get more basal moistening due to condensate,accumulating on the pipes. They should not be poured so as not to cause rot in the root system of plants.
- If the beds are designed for sowing seeds, you can equip a greenhouse, covering them with a film before germination. As soon as they get stronger, you can remove the film.
If we are talking about organic warm beds, then gardeners may wonder when it is better to build them. Here opinions differ. Someone is doing this in the spring, just before planting the seedlings. Someone is betting on the future and is engaged in equipping the beds in the fall.
Experts see this as some advantages.
- In autumn, a large amount of organic waste accumulates on the backyards. No need to burn or dispose of foliage, tops, dry branches and grass. They are ideal for laying in warm beds.
- By spring, all biomaterial pledged inside will begin to rot and forms an excellent heating for newly planted plants. In addition, the bed will sow, thicken, and the seedlings will sit firmly in the holes.
Regardless of climatic conditions, soil properties and light conditions, the equipment of warm beds in greenhouses will help to improve,speed up and prolong the yield of plants. Moreover, there are several options for arranging such constructions from which to choose. Currently, gardeners are widely using this technology, which from year to year brings a healthy, rich harvest.
For information on how to make warm beds in a greenhouse, see the next video.