Transparent plastic pipes: types and purpose
The rapid development of industry leads to the gradual replacement of traditional materials with new ones in all spheres of life, including the household. Plastic pipes have long pressed metal on the market of building materials and gradually became the de facto standard for laying household pipelines. Among all the varieties of plastic pipes, both in their appearance and in possible areas of application, transparent ones stand out in particular, so in this review we will look at the types and purpose of such products.
Special features
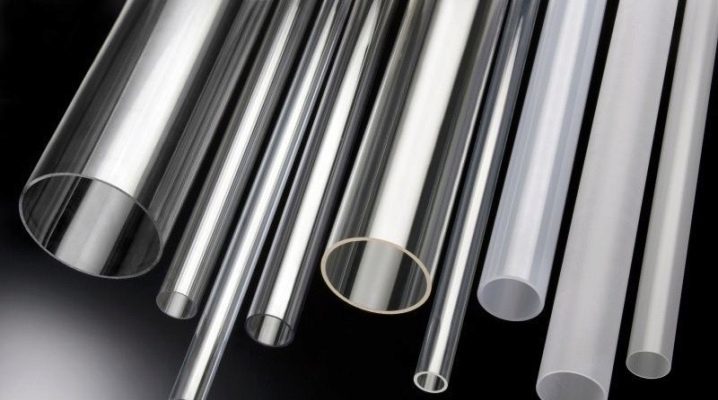
The key difference of transparent tubes from the rest of their types is, of course, optical properties. However, as for all other types of building materials, the very important characteristics of such products will be their strength, processability and resistance to external influences.These properties mainly depend on the material from which the pipe is made, and on the method of its manufacture. In this case, the only classic competitor of plastic transparent pipes are glass, which, with similar optical characteristics, are less impact resistant, much more mass and complexity of processing and manufacturing.
Species
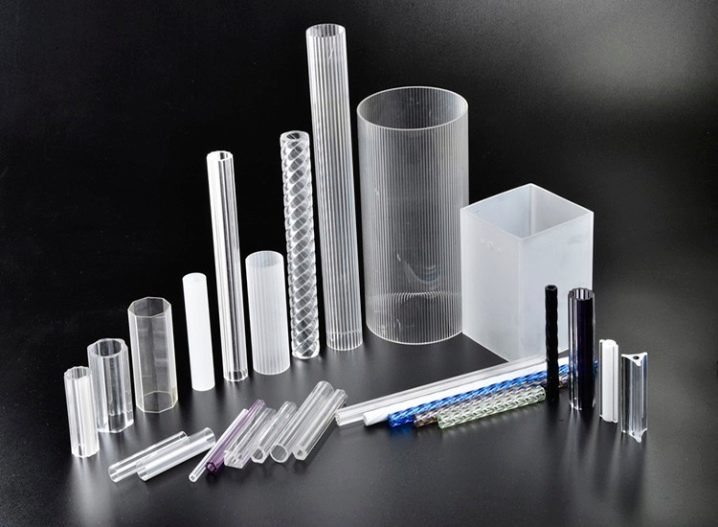
Currently the most Transparent pipes from 3 basic materials are widely used:
- Plexiglas (known as polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA);
- polycarbonate;
- polyvinyl chloride.
Externally, a pipe made of organic glass can be easily distinguished from other plastics. the presence of luster of the outer surface, while the inner surface of such pipes is usually matte.
Consider the advantages and disadvantages of each of the materials in more detail.
Plexiglass tubes
Plexiglas is a material that has long been known and familiar to many house craftsmen, and its widespread use in the USSR began in the second half of the 20th century. The transmittance of light by organic glass is up to 0.92, which is not inferior and even exceeds the properties of ordinary glass (from 0.85 to 0.9).At the same time, the weight of plexiglass is 2.5 times less than that of the ordinary, and the impact strength is 5 times higher. Even when destroyed, organic glass does not form dangerous sharp fragments. PMMA is not afraid of high humidity, does not decompose known microbes, is resistant to cold and many aggressive chemicals (oils, petroleum products, most alkalis and some acids).
Due to the relative softness of this material, it lends itself to almost the same types of processing.as wood - it can be cut, drilled and sawn, self-tapping screws twist well into it. Since PMMA belongs to the class of thermoplastics, products made from this material heated to 120 ° C can be hot molded - they can be given any desired shape that persists after cooling.
The main disadvantages of this material are low hardness, leading to ease of damage to its surface, solubility when exposed to alcohols and acetone, low heat resistance (even at 60 ° C PMMA loses resistance to deformation, the material melts at 160 ° C, at 260 ° C it burns, and heating to temperatures above 300 ° C results in the release of harmful methyl methacrylate during combustion).All this limits the range of application of such pipes to structures that will not be exposed to high internal pressure and elevated temperatures.
Polycarbonate pipes
Although for the first time polycarbonate was synthesized at the end of the 19th century, its industrial production in the form of sheet material began only in the second half of the 70s of the 20th century in Israel. Since then, the production of this material and products from it has been steadily increasing, due to its unique properties.
Polycarbonate combines all the benefits of organic glass (slightly inferior only in transparency - 0.9 against 0.92) with a significantly greater resistance to all types of external influences, including fire resistance. Its mechanical strength is 10 times higher than that of PMMA, and it weighs almost as much. Higher hardness of this material leads to increased resistance to all types of damage, including superficial ones. This material transfers low temperatures in the same way as Plexiglas, but to increased temperatures it is almost 2 times more resistant, therefore the allowable working temperature range of polycarbonate pipes is from - 60 ° C to + 120 ° C, which allows using it for external designs, and also for transportation of liquids with high temperature.
Although polycarbonate and harder plexiglass, but still well lends itself to machining and drilling, and increased heat resistance allows you to apply to it and welding. In addition, polycarbonate is resistant not only to acids and alkalis, but also to most types of alcohols and salts. In general, this material is chemically inert with respect to most materials, which makes it possible to use it for transporting liquids in the food and chemical industries.
Due to the increased strength of the product made from this polymer, they perfectly cope with the high pressure of the transported medium - for example, a polycarbonate pipe with a diameter of 25 mm transfers pressure up to 8 MPa, and with a diameter of 50 mm - up to 3 MPa.
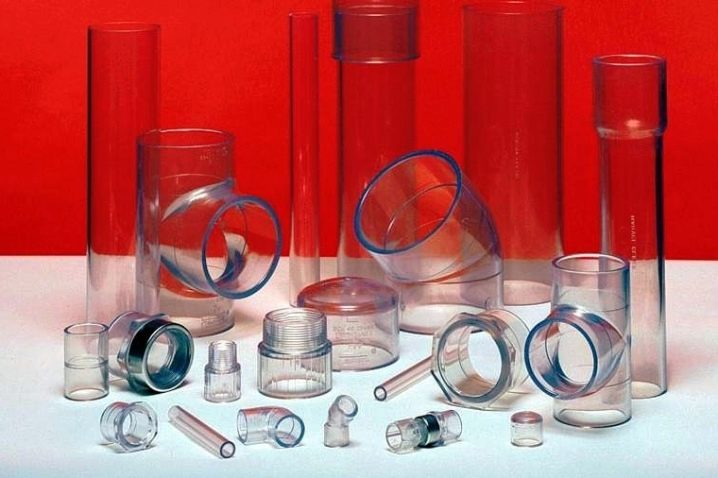
PVC pipes
PVC is the softest and least durable of all materials from which transparent pipes are made. The permissible temperature range of operation of such pipes is from - 15 ° C to 60 ° C, while heating above 110 ° C leads to the release of gaseous hydrogen chloride, which when dissolved in water forms hydrochloric acid. But PVC practically does not burn in the air environment. With prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays, polyvinyl chloride can decompose, to protect against this, special substances are introduced into its composition,which leads to turbidity only the outer layer. The transparency of PVC at the same time, of course, decreases. This combination of properties limits the use of transparent PVC pipes only decorative products used indoors.
But PVC is very easy to bend without heating. (which means that it is easy for him to give the required form), his service life in standard conditions is about 50 years, its installation and maintenance are extremely simple, and the specific gravity is only slightly higher than that of PMMA.
Production methods
Most thermoplastic products, including transparent pipes, are manufactured by two main methods, namely extrusion and casting.
Extrusion is the extrusion of pre-heated plastic. through the hole required (sheet, ring) form using a press. The use of this method allows to obtain a large variety of shapes and sizes of parts due to a small decrease in their mechanical and chemical resistance.
Of all the variety of casting methods for pipe production, centrifugal has become the most common. This method differs in that the injection mold is located in a rotating centrifuge,as a result, the liquid plastic is evenly distributed along its walls under the action of centrifugal force.
Application
In contrast to the opaque polymer pipes, which have long won positions during the conduction of water, gas and heat pipes, transparent plastic pipes are usually not used for transporting liquids and gases in everyday life. The main scope of such products in the home is their use in the design of premises and in the manufacture of various lighting fixtures. The situation is somewhat different in industry, where transparent polycarbonate pipes are used to transport drugs and chemical reagents, in food production, when the chemical inertness of the pipe material and the ability to control the appearance of the liquid at all stages of production are important.
Transparent tubes in design
PMMA and polycarbonate pipes are supplied not only in a purely transparent version, but also with the addition of various dyes, and their surface can be both shiny and matte. This opens up huge opportunities for their use in the design and creation of unique lighting.
Nowadays, matt-shaped profile diffusers are widely used for LED lamps made of polycarbonate tubes., the advantage of which is high durability and the ability to manufacture products of any shape. The combination of pipes of different shapes, colors and sizes allows you to create the most bizarre compositions. Apply such lamps and in the design of residential premises, and for outdoor advertising.
Transparent products are used - especially from polycarbonate - and for the decoration of premises both in the form of art objects (sculptures, fountains), and as parts of furniture or stairways.
PVC pipes are often used to create bright and comfortable Christmas garlands.
PMMA pipes are widely used in aquarium systems.
Corked polycarbonate pipes are used in trade as containers for various goods. Similar pipes are used to create various souvenirs.
The high strength of polycarbonate pipes allows their use as protective and anti-vandal structures.
For information on which transparent plastic pipes are stronger, see the following video.