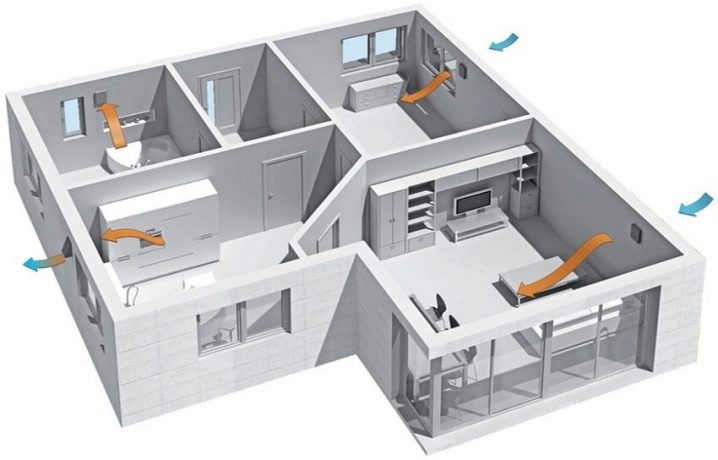
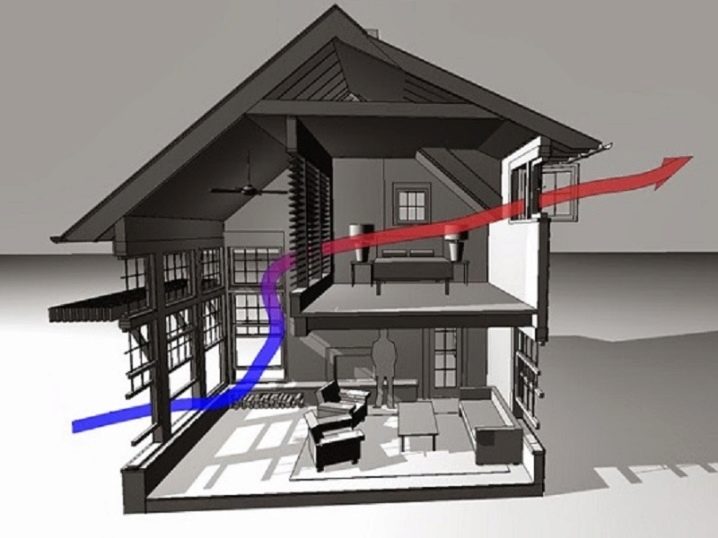
Classification of ventilation systems and their features

It is not always possible to get the necessary air flow through the windows and doors, sometimes weather conditions prevent this. And that is why special devices are created - ventilation complexes, which provide a solution to a similar problem. But a huge variety of practical conditions leads to the fact that these systems are divided into a number of types.
Normative documents
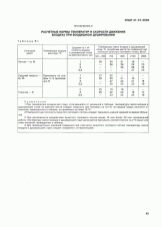
Such an important type of communications, like ventilation, is strictly regulated by regulations. Key requirements are contained in SNiP 41-01-2003. As stated by the developers of the act, it regulates:
- environmental performance;
- impact on the sanitary situation in the building;
- fire safety level;
- energy conservation;
- Stability of work under design conditions.
All these moments should be provided strictly, regardless of the specific format of ventilation and on the range of tasks solved by it. Recently, more and more attention has been paid to the improvement of mechanical ventilation and its connection with air-conditioning systems. The creators of the SNiP relied on the provisions of GOST relating to:
- acoustic safety (12.1.003-83);
- air properties in work and residential premises (12.1.005-88);
- standard cross-sectional dimensions of airborne equipment (24751-81);
- microclimate in residential and administrative buildings (30494-96).
The standard requirement for air supplied to living rooms is to warm to at least 15 degrees in winter. Public buildings and administrative facilities require at least 12 degrees of heat. And in the production shops are not allowed to supply air, the temperature of which would be less than 5 degrees. The design task may provide for a lower air temperature during the cold season. All pipelines are installed only so that they can be easily repaired or replaced.
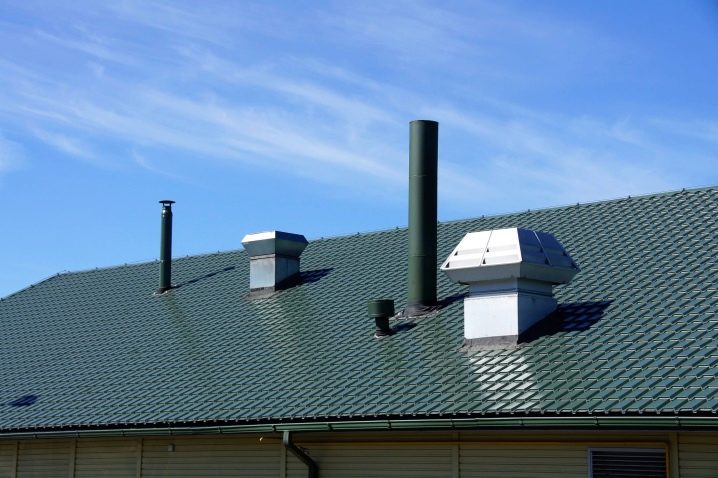
All openings for air-receiving devices can be placed at a height of at least 1 m above a stable line of snow cover. It is necessary to determine this parameter taking into account the data of meteorological services monitoring the weather in a certain area. Where sandstorms occur, these cameras should be surrounded by devices that trap harmful particles. Air receiving systems must be separate for each fire compartment. When calculating the need for air take the basis of the largest numbers.
System classification
By way of filing
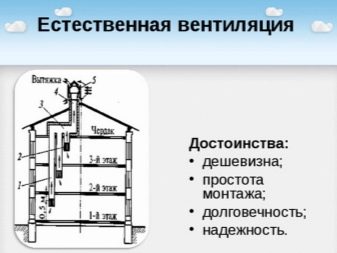
By this parameter, natural and artificial types of ventilation are distinguished. Natural movement is provided by:
- temperature differences between the outside and the air in the house;
- pressure differentiation between the room and the deflector on the roof;
- pressure created by the wind.
The first option is best used where there is a lot of heat. Most often we are talking about production plants, the air which contains a small amount of toxic gases and dust particles. Aeration will have to be abandoned if it requires sophisticated preparation of incoming air, as well as in the case when its intake provokes the appearance of mist, condensation.Natural ventilation, which works by means of an imbalance of pressure between two points, requires the creation of a difference in height of at least 3 m. It is advisable to install horizontal duct sectors no longer than 300 cm, to limit the rate of air movement to 1 m per second.
The wind system works in the case when parts of the building turned to the wind are subjected to increased pressure, and in the opposite place it is reduced. Naturally, the air rushes from a denser area to places where there is a vacuum; in order to get inside it requires the presence of openings in the fences The faster the wind flow, the greater the pressure difference, and therefore the air will flow inward in greater volume. Any of the described ventilation systems is characterized by simplicity and no need for electric current. But since the driving forces are very unstable and the air pressure turns out to be rather small, it will not be possible to count on a successful solution of the whole range of problems.
The output is the use of special equipment that facilitates and accelerates the movement of air over substantial distances. Increased possibilities of mechanized ventilation often turn into substantial costs for electrical energy. You can extract air from certain places or add it if necessary, regardless of unstable environmental conditions. Another advantage is the ability to complete processing, including increasing humidity or removing pollution. To eliminate problems, often use mixed ventilation, which is able to work in a forced or in a natural mode.
To destination
This parameter allows you to select the supply and exhaust systems. Names already eloquently characterize their essence. Thanks to the supply equipment, it is possible to provide clean outdoor air instead of mass to be removed. In certain cases, the incoming air is treated (cleaned, made more humid or heated). Exhaust systems are designed to clean the spent part of the air.
In practice, these two types of systems are used simultaneously., trying to ensure a balance between the flow of air and its discharge to the outside. There are cases when only a hood or inflow is mounted.In such situations, the main structural openings of the room itself or adjacent parts of the building are used to exchange air with the external environment. Developers can provide for the inflow and removal of the exhaust gas mixture for the entire facility as a whole. But sometimes their placement is used only in certain areas.
By way of air exchange
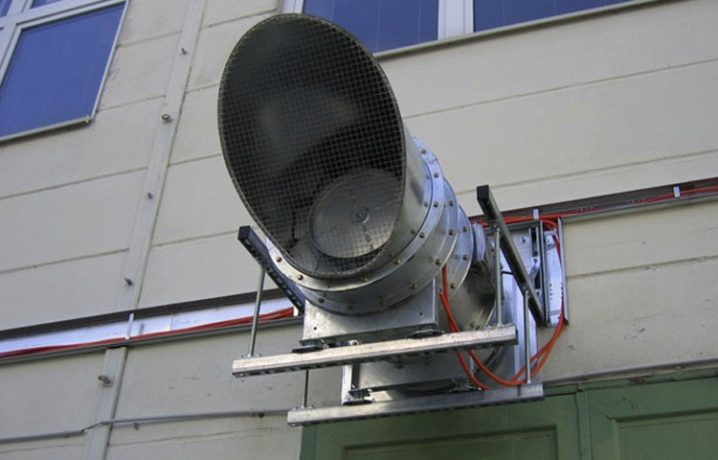
There are such types of air exchange as local, general, emergency, fire-fighting and combined options. Any system that delivers portions of air to specific places or removes contaminated mass from individual problem areas just gets into the category of local ventilation. A variant of the local flow are air showers. Like their water analogues, they direct the flow in a concentrated manner, increasing its speed. Basically, such systems are needed to reduce the heating of the workplace and cool the people themselves who are at risk of heat stroke.
The so-called air oases have become quite widespread. They are formed by separating certain parts of the room from the rest of its volume using mobile partitions.Each oasis should be supplied with relatively cold (compared to the ground mass) air flow. At industrial facilities where there are appliances and machines that create heat, air curtains are often used. The undoubted advantage of local ventilation is that it is more economical than capital systems.
But the use of such complexes in all parts of buildings is not always appropriate. After all, this greatly complicates the design and installation, requires careful coordination of separate ventilation segments between them. Therefore, even in serious enterprises, the main role belongs to the overall system. Local units are used only in those workplaces where there is a need for a special circulation mode. As for local extracts, they are needed so that local sources of pollution do not leak into the rest of the building.
Many options for removing localized systems have been developed:
- umbrellas;
- curtains;
- suction cabinets;
- housings on individual machines and so on.
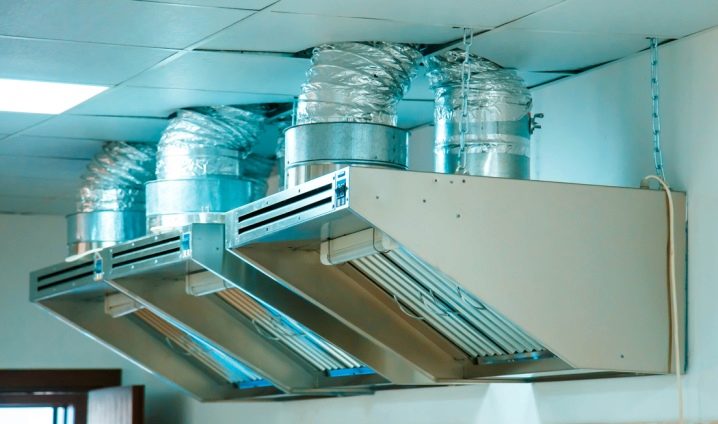
Suction devices are subject to very strict requirements. So, we must try to cover all the space that is subject to clogging.If this is not possible, it is necessary to ensure the removal from the largest possible part of the installation, creating harmful substances. Further, suction pumps must necessarily eliminate interference with the full operation of the enterprise as a whole and its individual employees.
To reduce energy consumption, it is required to direct harmful substances to the same place where they would go. Not open, but half-open suction is preferable. Their advantage is that it requires a much smaller amount of air to clean the atmosphere. Local exhaust hoods should be equipped at the entrance with devices that remove dust. Important: if the workflow covers the entire room or involves the movement of people, then a general ventilation system is needed.
A common exchanger allows you to evenly pull the air out of the room or just as evenly distribute it.
The following main tasks are solved:
- elimination of excess heat and moisture;
- lowering dangerous volumes of gaseous substances;
- maintenance of sanitary standards provided for in the design calculations;
- providing comfort for working in certain places.
If when collecting data for a project it turns outthat there is not enough heat in the room, the flow of general ventilation must be equipped with mechanical accelerators and devices that warm the air. It is desirable in this case to release the air mass from the dust. After all, any heating equipment, with rare exceptions, only increases its quantity. And if dust particles fall into open fire or on a heated surface, an unpleasant smell can appear. Since emissions at a number of productions contain gases of high density, dust, and the equipment itself produces almost no heat, in such cases they install floor or underground pipelines.
But many industrial objects work in such a way that many different types of harmful substances appear. In this case, usually they still enter the room unequally. In this situation, it is necessary to combine local and general ventilation. Separately, these two systems will not cope, even if their design and installation will be carried out perfectly.
By design
There is a simple gradation on the channel and not having channel system. Channels called any air ducts.
Channelless options are quite diverse:
- in some cases, fans are mounted directly in the walls;
- in others - the same fans are hidden in the ceiling;
- in the third, the natural movement of air masses is used.
Natural and mechanical
It is useful to more deeply consider the differences in the device of natural and mechanized ventilation. In any case, you first need to calculate the intensity of air exchange, find out what should be the cross section of the air channels. It is believed that the natural type of ventilation is more comfortable for people. In addition, the limitation of the flow rate allows almost no fear of drafts. Namely, this factor is the "initiator" for many respiratory diseases.
But the problem is that reducing the air velocity requires (with the same volume of it) increasing the size of the channel. This not only complicates the work and increases the cost of it. Often, it is simply not possible to apply pipelines of the required size. This creates technical or design difficulties. Because just like that to abandon mechanical devices is impractical.
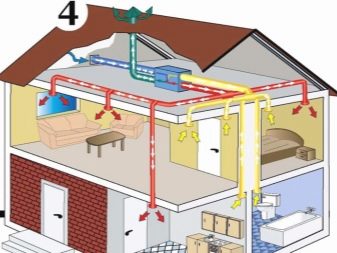
The general between the natural and mechanical movement of air is that you need to think about the flow of it inside a house or a large building. Usually, this goal is achieved by installing special grills in the doors on the desired flow path. Professionals believe that the dirtiest place should be purged last. For a residential building such a zone is a sanitary unit; it is preceded by a kitchen.
If the grid option is not suitable, you can leave a gap from the bottom of the door to the floor. Its size should be uniform - at least 2 cm along the entire length, regardless of the type of flooring and the intended use of the rooms to be connected. When the grille (gap) is not, no investment in the ventilation system will not be justified. If the bathroom has a hood, the pressure increase will complicate the opening of the door. Important: when taking into account the natural flow of air, it is necessary to take into account that part of it that sneaks through the slots and openings in external walls and other structures.
If wooden windows are not tight (and they still remain in many places), in an hour after 1 square. m of surface they will go inside to 20 kg of air. In private houses and apartments, the area of which does not exceed 150 square meters. m, this is enough to meet hygienic needs.Especially when you consider that some inflow goes through loose joints on the doors and even through walls. If the rooms are glazed with modern plastic, aluminum windows, they are much more airtight. But here it is necessary to introduce amendments to the intensity of airing and microairing in accordance with the manufacturer's documentation.
General Mechanical Drive
Fresh air
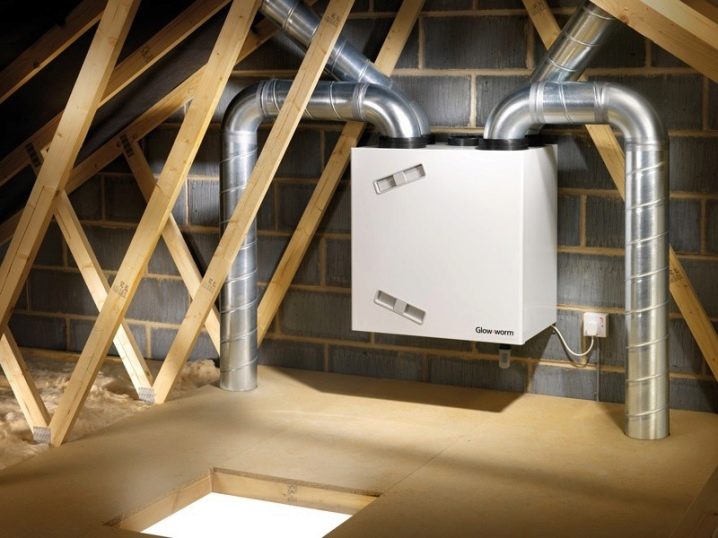
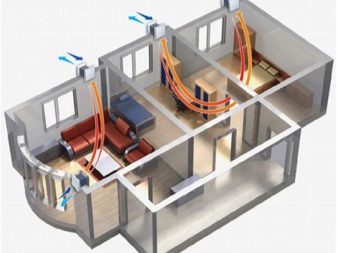
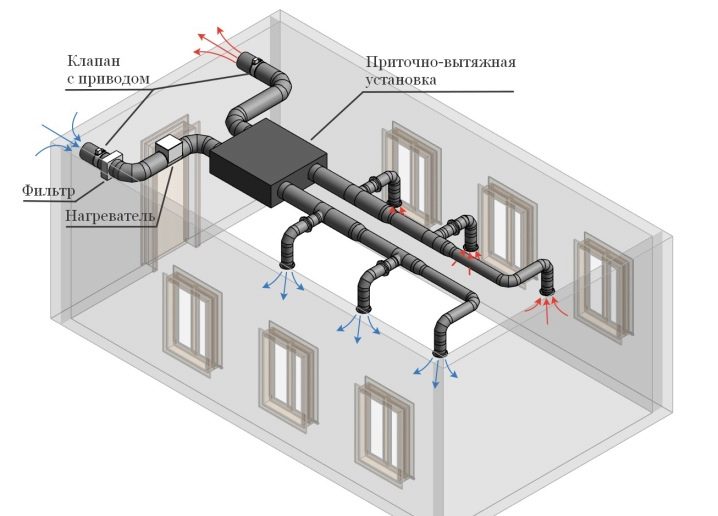
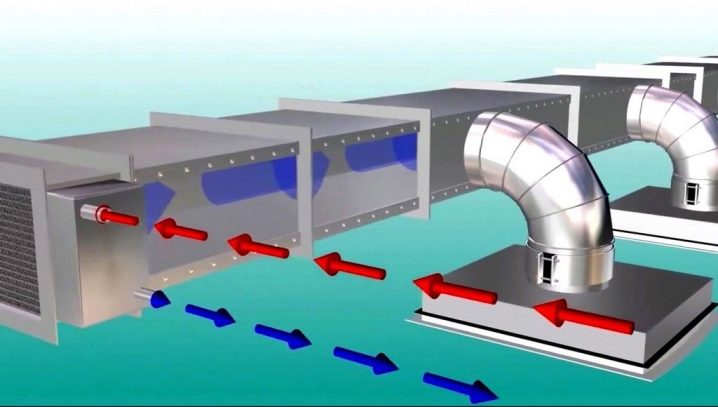
The inflow-type constructions for the most part have duct design and consume a fairly substantial amount of electricity. But it provides a full supply of air even the most inaccessible places. Therefore, the cost of arranging such communications in the shortest possible time pays off. Since the rate of air pumping with the help of mechanical systems is quite high, the inflow should compensate for all that the withdrawal took. An exception is made only for places where there is a toxic or odorless substance.
At such points, less air is necessarily added than is extracted from there. To compensate for the difference, use paging through the windows or from areas where the atmosphere is cleaner. The basic components are:
- intake apparatus;
- cleaner;
- air heater;
- fan;
- air lines;
- tubes for nozzles with the necessary nozzles.
There are situations when it is not necessary to heat the incoming air. In this case, it bypasses the heater and moves along the bypass route. In the process of designing, the supply of mechanical ventilation is equipped mainly with clean or almost clean rooms. For air pumping can be used ejectors or conventional fans. The choice between them in a particular case is made for engineering reasons.
General exhaust
General Exhaust Exhaust - In the process of calculating such systems, the goal is to find the configuration, which would allow, after replacing the displaced air, to reduce the concentration of harmful substances to the level of the MPC or less. Use of systems with elongated air ducts is allowed. When the total length of such a pipeline is more than 30-40 m, it is legitimate to fear excessive pressure loss. You can compensate them by replacing the axial fans with centrifugal, which drive the air stronger. In some cases, elements that provide aeration come to the aid of the general exchange drawing system.
Supply and exhaust
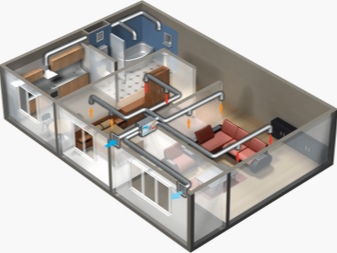
The forced-air and exhaust option favorably stands out in comparison with already called excellent performance. There are two ways to form a supply and exhaust system.
In the first scheme, the air is mixed as follows:
- a fan spinning at high speeds draws fresh portions from the street;
- in the room the old and new air are mixed;
- the excess evaporates through a special valve and a pipe connected to it.
To accommodate the fans choose a position on the ceiling or on himself. But there is another solution that involves pushing out the exhaust air with a leaking mass. There will already need fans with low speed, and they are placed below. An exhaust pipe is mounted on the outer wall, which is connected to the exhaust valves using special channels. Valves and channels are located on top.
When the fan is working, new air portions are sucked in from the outside. That part of it, which is already in the room, manages to warm up. At the same time it becomes easier, rises to the ceiling, where it is mechanically pushed through the valve. It is easy to understand why such a construction is best implemented in homes with high ceilings.In order not to provoke a pressure difference, it is necessary to balance the pulling and sucking elements very well, otherwise their work will be poorly coordinated.
An important point: the formation of areas with high blood pressure helps to eliminate the ingress of bad odors from kitchens and bathrooms into adjacent rooms. In these places, the inflow should go more actively than air suction. In most regions of Russia, the addition of supply and exhaust ventilation with heat recovery means is appropriate. Some of these devices reduce the total heat loss by removing air masses by almost. In fact, heat recovery is provided by heat exchangers, in which the outside air absorbs some of the heat from the outgoing mass, without mixing with it.
The next logical step is to equip the recuperator units with devices that increase the humidity of the air and additional filters. But the problem is that not all specialists can even mount simple devices. Moreover, it is impossible to create ventilation with your own hands, which uses a heat exchanger with additional options. They also complicate billing and subsequent maintenance.So before making a final decision it is necessary to weigh all these circumstances.
In case of an accident
If you need to dismantle the broken ventilation and then restore it, you need to get down to business very seriously. First you need to find out exactly what type of box installed in a particular room. The decisive test, which accurately identifies serious malfunctions, is done by hand, without the involvement of experts. It is only necessary to see whether the light deviates towards the air channel or not.
Restoration work begins with the analysis of floors and walls. It is very important to select exactly those materials that meet the standard requirements. Most often used slabs of gypsum and blocks based on foam concrete. Do not overly narrow the ventilation box so as not to perform work from scratch. The convenience of individual materials does not justify their use for the formation of ventilation.
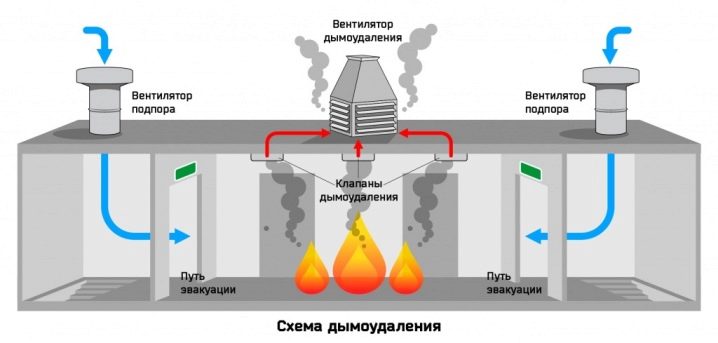
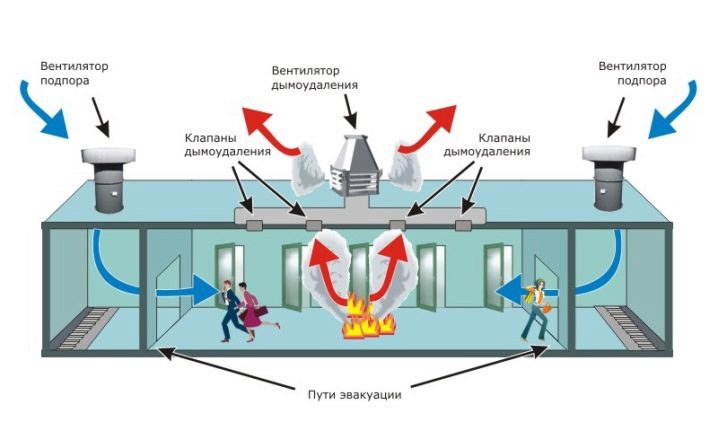
Against smoke
Fire fighting ventilation has a special role. Removing smoke is especially important in areas actively used by people and on escape routes. First, they make up an evacuation plan, and then, in accordance with it, a scheme of smoke evacuating ventilation is being prepared. Appropriate systems should be made separate from other devices. Be sure to install anti-smoke channels:
- in trade institutions;
- in high-rise buildings of any kind;
- in administrative buildings;
- in office facilities, educational and cultural institutions;
- in hotels and hostels.
Recently, corrections have been made to the federal regulatory framework, which prescribes the installation of anti-smoke channels in underground parking lots, in public garages and in warehouses. Smoke removal designs must guarantee:
- quick, smooth and efficient evacuation;
- saving as long as possible the integrity of the property;
- maintenance of relatively favorable (as far as possible in case of fire) conditions for the actions of rescue teams;
- blocking the movement of gaseous and solid products of combustion inside the building, their exit to the outside.
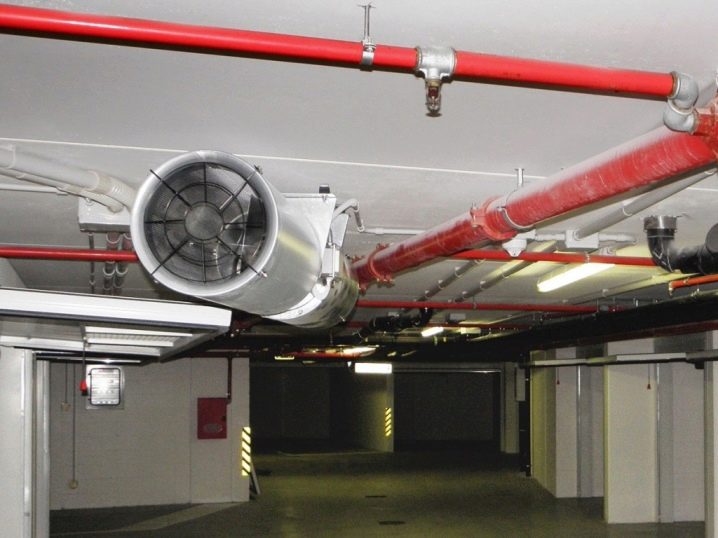
Often practiced forcing air under high pressure. This is ensured by the use of special fans. Depending on the specific conditions, harmful substances can be pulled out both naturally and mechanically. But almost always they use exactly the special mechanics to speed up the work and increase efficiency.Most often, the quality check of the installation of fire-prevention ventilation systems is combined with a training fire alarm.
Types of ducts
The channels through which the air flow is divided by:
- geometry;
- applied material;
- specific characteristics;
- block binding method.
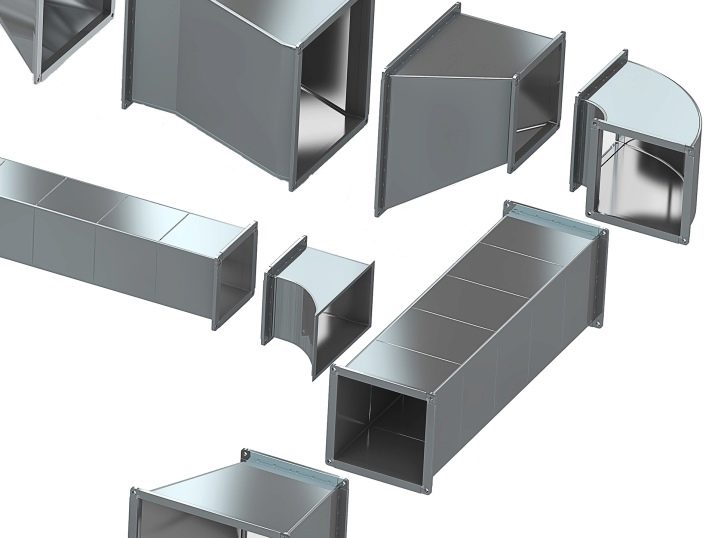
The rectangular type of duct is practical, but inside the air forms a whirlwind. If we apply a rounded vented channel, the flow will begin to slide freely. This is only achieved when the surface is sufficiently smooth. As for the docking method, it determines the financial and time costs, and at the same time with them the quality of the seams being created. If you want to stretch a round tube, apply a bandage.
For the production of pipes used:
- stainless and galvanized steel grades;
- polyethylene;
- metal plastic;
- special fabrics;
- fiberglass;
- aluminum.
Decisive in choosing between these options are their thermal and mechanical resistance. The scope is determined by the rigidity of the structure. The pressure is considered low if it does not exceed 0.9 kPa. Announce high pressure over 2 kPa.Intermediate indicators fall into the middle category.
For residential and industrial premises
The differences between ventilation in these cases are connected not only with the fact that there are few harmful reagents in the houses. The difference is due to the fact that the volume of pumped air is very different. In industrial buildings, ventilation should ensure the purification of the internal atmosphere from:
- dust particles;
- microscopic inclusions;
- toxic fumes.
Relatively recently, in the room and even on the balcony were used for airing loose places in wooden frames. But modern ventilation systems, although they can successfully replace them with full glazing, work well only in the case of high-quality insulation. First of all, warming the structure is required outside to reduce the formation of condensate. The most frequent type of ventilation in this place is intake-exhaust valves, which are:
- almost no eye;
- occupy a minimum of space;
- exclude the appearance of drafts;
- do not require power supply;
- managed by simple devices.
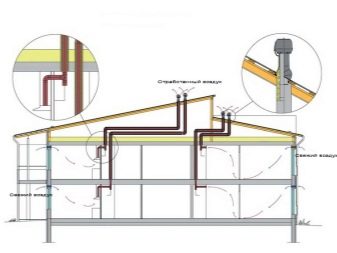
The arrangement of ventilation channels in the wall of a warm attic has its own characteristics.Roofing aerators direct the supply air mass in the area of the eaves. Most people choose soffits with special holes to be installed in the lower lobe of the eaves. Perforated designs, passing fresh blows, block the passage of insects. Thanks to the spotlights, it is possible to create a flawless look and guarantee functionality.
Cold attics are ventilated predominantly by the means they create on their own. For this purpose, the passage of air through:
- grilles and gable windows;
- roof ridges;
- skates;
- eaves of eaves.
Channel and channelless systems
Channelless ventilation devices do not give a good result in all cases. Not even every apartment can be ventilated in this way. But the garages, utility rooms - completely. If the building is divided into a number of zones that differ in their parameters, it will be necessary to use only channel complexes. Important: the channelless configuration is completely compatible, as well as having pipelines, with mechanical and natural encouragement of the course of air.
The natural channelless method of ventilation is in principle uncontrollable, it does not allow controlling the process. In addition, it leads to substantial heat consumption. Mechanical influx without the use of channels implies the use of either special fans or air conditioners. By execution, this is similar to the oases and veils already described. Due to the high power of the necessary devices that drive the flow, it is necessary to install devices that suppress the sound.
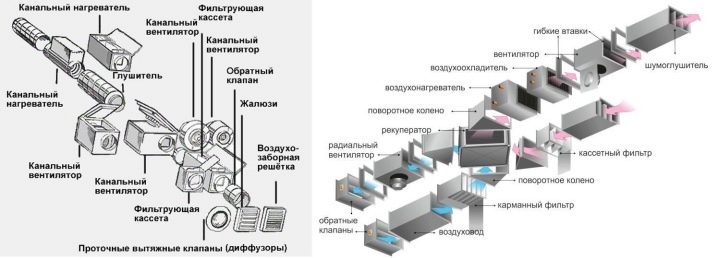
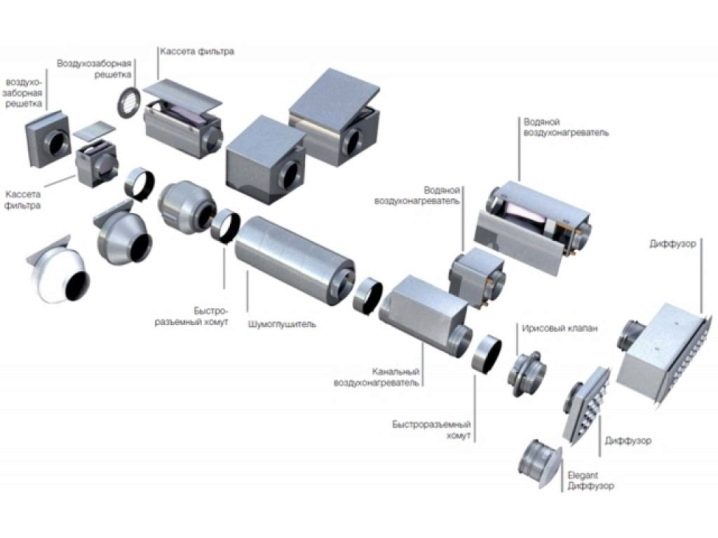
Main elements
Among the indispensable parts of the ventilation system are exhaust and air inlet openings. Their size is determined individually, taking into account the need for inflow and discharge. According to the size of the holes, both the grids and the piping are selected. To hold open (hanging without solid support) areas, special brackets are used to hold the channel to the wall or ceiling. The role of adapters is to interconnect pipes of different sections, in the formation of turns and intersections.
Controllers and control panels are used mainly in cottages and other serious objects. Additionally, you can apply:
- ceiling diffusers;
- gates;
- axial and radial fans;
- tubular chamber silencers;
- water and electric heaters.
To learn how to install ventilation systems in the house with your own hands, see the following video.